Valofane
 | |
| Clinical data | |
|---|---|
| ATC code | none |
| Identifiers | |
| |
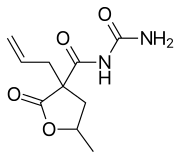
| Synonyms | N-carbamoyl-5-methyl-2-oxo-3-prop-2-enyloxolane-3-carboxamide |
| CAS Number |
3258-51-3 |
| PubChem (CID) | 71122 |
| ChemSpider |
64272 |
| UNII |
X71N6E5IPO |
| ChEMBL |
CHEMBL2104479 |
| ECHA InfoCard | 100.019.871 |
| Chemical and physical data | |
| Formula | C10H14N2O4 |
| Molar mass | 226.229 g/mol |
| 3D model (Jmol) | Interactive image |
| |
| |
| | |
Valofane is a sedative drug structurally related to the barbiturates[1] and similar drugs such as primidone. It is metabolised once inside the body to form the barbiturate proxibarbital (proxibarbal) and is thus a prodrug.[2]
References
- ↑ Traversa U, Puppini P, Jacquot C, Vertua R. Effect of an atypical barbiturate, the 2-allophanyl-2-allyl-4-valerolactone (valofan), on exploratory behaviour and brain serotonin concentrations in mice. Journal de Pharmacologie. 1985 Jul-Sep;16(3):279-90.
- ↑ Lambrey B, Compagnon PL, Jacquot C. Pharmacokinetics of 14C-2-allophanyl-2-allyl -gamma-valero-lactone: a prodrug of proxibarbal in rats. European Journal of Drug Metabolism and Pharmacokinetics. 1981;6(3):161-9.
| Alcohols | |
|---|---|
| Barbiturates |
|
| Benzodiazepines |
|
| Carbamates | |
| Flavonoids | |
| Imidazoles | |
| Kava constituents |
|
| Monoureides |
|
| Neuroactive steroids |
|
| Nonbenzodiazepines |
|
| Phenols | |
| Piperidinediones | |
| Pyrazolopyridines | |
| Quinazolinones | |
| Volatiles/gases |
|
| Others/unsorted |
|
See also: GABAergics | |
This article is issued from Wikipedia - version of the 4/2/2016. The text is available under the Creative Commons Attribution/Share Alike but additional terms may apply for the media files.