Aprobarbital
 | |
 | |
| Clinical data | |
|---|---|
| AHFS/Drugs.com | Micromedex Detailed Consumer Information |
| ATC code | N05CA05 (WHO) |
| Legal status | |
| Legal status |
|
| Identifiers | |
| |
| Synonyms | aprobarbital, Oramon, allylpropymal, Alurate, 5-isopropyl- 5-allylbarbituric acid |
| CAS Number |
77-02-1 |
| PubChem (CID) | 6464 |
| DrugBank |
DB01352 |
| ChemSpider |
6221 |
| UNII |
Q0YKG9L6RF |
| KEGG |
D00698 |
| ChEBI |
CHEBI:2791 |
| ChEMBL |
CHEMBL7863 |
| Chemical and physical data | |
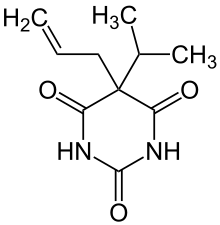
| Formula | C10H14N2O3 |
| Molar mass | 210.23 g/mol |
| 3D model (Jmol) | Interactive image |
| |
| |
| (verify) | |
Aprobarbital (as known in the United States, or aprobarbitone (as known elsewhere), sold as Oramon, Somnifaine, and Allonal, is a barbiturate derivative invented in the 1920s by Ernst Preiswerk. It has sedative, hypnotic and anticonvulsant properties, and was used primarily for the treatment of insomnia.[1] Aprobarbital was never as widely used as more common barbiturate derivatives such as phenobarbital and is now rarely prescribed as it has been replaced by newer drugs with a better safety margin.
See also: Alphenal
References
- ↑ Reddemann H, Turk E. Oramon poisoning in infancy and childhood. Observations on 12 aprobarbital poisonings (German). Das Deutsche Gesundheitswesen. 1966 May 12;21(19):878-81.
| Alcohols | |
|---|---|
| Barbiturates |
|
| Benzodiazepines |
|
| Carbamates | |
| Flavonoids | |
| Imidazoles | |
| Kava constituents |
|
| Monoureides |
|
| Neuroactive steroids |
|
| Nonbenzodiazepines |
|
| Phenols | |
| Piperidinediones | |
| Pyrazolopyridines | |
| Quinazolinones | |
| Volatiles/gases |
|
| Others/unsorted |
|
See also: GABAergics | |
This article is issued from Wikipedia - version of the 6/8/2016. The text is available under the Creative Commons Attribution/Share Alike but additional terms may apply for the media files.