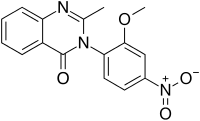
Nitromethaqualone
 | |
| Clinical data | |
|---|---|
| ATC code | none |
| Identifiers | |
| |
| CAS Number | 340-52-3 |
| PubChem (CID) | 63339 |
| ChemSpider | 57006 |
| Chemical and physical data | |
| Formula | C16H13N3O4 |
| Molar mass | 311.29 |
| 3D model (Jmol) | Interactive image |
| |
Nitromethaqualone[1] is an analogue of methaqualone that has similar sedative and hypnotic properties.[2] It is significantly more potent (10x) compared to the parent compound; the typical dose is approximately 25 mg.[3] However, the aromatic nitro group is metabolised to the corresponding aniline, which proved to be a mutagen.[3] As a consequence, nitromethaqualone was not developed further due to toxicity concerns.
References
- ↑ US patent 3162634, Klosa, J. (Berlin, Germany), "2-Methyl-3-(2'-methyl-3'-chlorphenyl)-quinazolone-(4)", issued 1964-12-22
- ↑ Szirmai, A. (1963). "(title in German)" [Pharmacological and Therapeutic Studies with a New Quinazolone Derivative, Nitromethaqualone]. Therapeutische Umschau (in German). 20: 542–546. PMID 14101319.
- 1 2 van Boven, M.; Daenens, P. (1982). "Biotransformation and Excretion of Nitromethaqualone in Rats and Humans". Journal of Pharmaceutical Sciences. 71 (10): 1152–1157. doi:10.1002/jps.2600711019. PMID 7143214.
| Alcohols | |
|---|---|
| Barbiturates |
|
| Benzodiazepines |
|
| Carbamates | |
| Flavonoids | |
| Imidazoles | |
| Kava constituents |
|
| Monoureides |
|
| Neuroactive steroids |
|
| Nonbenzodiazepines |
|
| Phenols | |
| Piperidinediones | |
| Pyrazolopyridines | |
| Quinazolinones | |
| Volatiles/gases |
|
| Others/unsorted |
|
See also: GABAergics | |
This article is issued from Wikipedia - version of the 9/2/2015. The text is available under the Creative Commons Attribution/Share Alike but additional terms may apply for the media files.