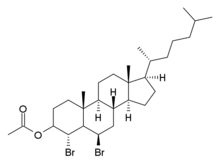
Acebrochol
 | |
| Clinical data | |
|---|---|
| ATC code | none |
| Identifiers | |
| |
| CAS Number |
514-50-1 |
| PubChem (CID) | 10952056 |
| ChemSpider |
9127276 |
| UNII |
7XZB016MY5 |
| ChEMBL |
CHEMBL2104033 |
| Chemical and physical data | |
| Formula | C29H48Br2O2 |
| Molar mass | 588.498 g/mol |
| 3D model (Jmol) | Interactive image |
| |
| |
| | |
Acebrochol (INN),[1] also known as cholesteryl acetate dibromide or 5α,6β-dibromocholestan-3β-ol acetate, is a neuroactive steroid which was described as a sedative and hypnotic but was never marketed.[2]
See also
References
- ↑ "INN - acebrochol". Mednet. Whorld Health Organisation (WHO). Retrieved 10 August 2015.
- ↑ R.A. Hill; H.L.J. Makin; D.N. Kirk; G.M. Murphy (23 May 1991). Dictionary of Steroids. CRC Press. pp. 229–. ISBN 978-0-412-27060-4.
| Alcohols | |
|---|---|
| Barbiturates |
|
| Benzodiazepines |
|
| Carbamates | |
| Flavonoids | |
| Imidazoles | |
| Kava constituents |
|
| Monoureides |
|
| Neuroactive steroids |
|
| Nonbenzodiazepines |
|
| Phenols | |
| Piperidinediones | |
| Pyrazolopyridines | |
| Quinazolinones | |
| Volatiles/gases |
|
| Others/unsorted |
|
See also: GABAergics | |
This article is issued from Wikipedia - version of the 11/2/2016. The text is available under the Creative Commons Attribution/Share Alike but additional terms may apply for the media files.