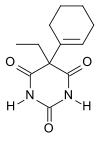
Cyclobarbital
 | |
 | |
| Clinical data | |
|---|---|
| AHFS/Drugs.com | International Drug Names |
| Routes of administration | Oral (tablets) |
| ATC code | N05CA10 (WHO) |
| Legal status | |
| Legal status |
|
| Pharmacokinetic data | |
| Metabolism | Hepatic |
| Excretion | Renal |
| Identifiers | |
| |
| CAS Number |
143-76-0 |
| PubChem (CID) | 5838 |
| ChemSpider |
5632 |
| UNII |
0M8A98AD9H |
| KEGG |
D07323 |
| ChEMBL |
CHEMBL268164 |
| ECHA InfoCard | 100.000.127 |
| Chemical and physical data | |
| Formula | C12H16N2O3 |
| Molar mass | 236.267 g/mol |
| 3D model (Jmol) | Interactive image |
| |
| |
| | |
Cyclobarbital, also known as cyclobarbitol or cyclobarbitone, is a drug which is a barbiturate derivative.[1] It is primarily available in fixed-dose combination with diazepam under the brand name Reladorm (100 mg cyclobarbital + 10 mg diazepam) and is used to treat insomnia in Russia.[2]
References
- ↑ Breimer, D. D.; Winten, M. A. (1976). "Pharmacokinetics and relative bioavailability of cyclobarbital calcium in man after oral administration". European journal of clinical pharmacology. 09 (5–6): 443–450. PMID 989475.
- ↑ "Russian State Register of Medicines. Registration Certificate: Reladorm (diazepam + cyclobarbital). Revised 02 Sep 2013" (in Russian). Retrieved 6 March 2016.
This article is issued from Wikipedia - version of the 4/2/2016. The text is available under the Creative Commons Attribution/Share Alike but additional terms may apply for the media files.