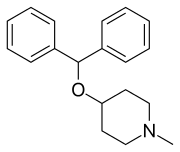
Diphenylpyraline
 | |
| Clinical data | |
|---|---|
| AHFS/Drugs.com | International Drug Names |
| Routes of administration | Oral, Topical |
| ATC code | R06AA07 (WHO) |
| Legal status | |
| Legal status |
|
| Pharmacokinetic data | |
| Biological half-life | 24–40 hours[1] |
| Identifiers | |
| |
| Synonyms | 4-(diphenylmethoxy)-1-methyl-piperidine |
| CAS Number |
147-20-6 |
| PubChem (CID) | 3103 |
| IUPHAR/BPS | 7165 |
| DrugBank |
DB01146 |
| ChemSpider |
2992 |
| UNII |
33361OE3AV |
| KEGG |
D07862 |
| ChEBI |
CHEBI:59788 |
| ChEMBL |
CHEMBL1492 |
| ECHA InfoCard | 100.005.170 |
| Chemical and physical data | |
| Formula | C19H23NO |
| Molar mass | 281.392 g/mol |
| 3D model (Jmol) | Interactive image |
| |
| |
| (verify) | |
Diphenylpyraline (DPP; sold as Allergen, Arbid, Belfene, Diafen, Hispril, Histyn, Lergobine, Lyssipol, Mepiben, Neargal) is a first-generation antihistamine with anticholinergic effects of the diphenylpiperidine class.[2][3][4] It is marketed in Europe for the treatment of allergies.[2][3][5] DPP has also been found to act as a dopamine reuptake inhibitor and produces hyperactivity in rodents.[6] It has been shown to be useful in the treatment of Parkinsonism.[7]
Synthesis
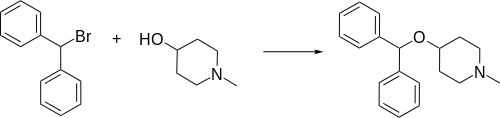
Diphenylpyraline, 4-diphenylmethoxy-1-methylpiperidine, is synthesized by alkylating 4-hydroxy-1-methylpiperidine with benzhydrylbromide.
Trade names
Arbid, Dafen, Dayfen, Histyn, Hispril, etc.
References
- ↑ Graham G, Bolt AG (June 1974). "Half-life of diphenylpyraline in man". Journal of Pharmacokinetics and Biopharmaceutics. 2 (3): 191–5. doi:10.1007/BF01059761. PMID 4156058.
- 1 2 Swiss Pharmaceutical Society (2000). Index Nominum 2000: International Drug Directory (Book with CD-ROM). Boca Raton: Medpharm Scientific Publishers. ISBN 3-88763-075-0.
- 1 2 Puhakka H, Rantanen T, Virolainen E (1977). "Diphenylpyraline (Lergobine) in the treatment of patients suffering from allergic and vasomotor rhinitis". J Int Med Res. 5 (1): 37–41. PMID 14039.
- ↑ Kubo N, Shirakawa O, Kuno T, Tanaka C (March 1987). "Antimuscarinic effects of antihistamines: quantitative evaluation by receptor-binding assay". Japanese Journal of Pharmacology. 43 (3): 277–82. doi:10.1254/jjp.43.277. PMID 2884340.
- ↑ Hruby, Victor J.; Ruben Vardanyan; Vardanyan, ۊRuben (2006). Synthesis of essential drugs. Amsterdam: Elsevier. ISBN 0-444-52166-6.
- ↑ Lapa G, Mathews T, Harp J, Budygin E, Jones S (2005). "Diphenylpyraline, a histamine H1 receptor antagonist, has psychostimulant properties". Eur J Pharmacol. 506 (3): 237–40. doi:10.1016/j.ejphar.2004.11.017. PMID 15627433.
- ↑ Ohno T, Kobayashi S, Hayashi M, Sakurai M, Kanazawa I (2001). "Diphenylpyraline-responsive parkinsonism in cerebrotendinous xanthomatosis: long-term follow up of three patients". J Neurol Sci. 182 (2): 95–7. doi:10.1016/S0022-510X(00)00441-X. PMID 11137513.
- ↑ H.K. Lawrence, R. Kapp, U.S. Patent 2,479,843 (1949).
- ↑ W.A. Schuler, DE 934890 (1951).
| Aminoalkyl ethers |
|
|---|---|
| Substituted alkylamines | |
| Substituted ethylenediamines |
|
| Phenothiazine derivatives | |
| Piperazine derivatives | |
| Others for systemic use |
|
| For topical use | |
| Dopaminergics |
| ||||||||||||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Anticholinergics | |||||||||||||||||||
| Others | |||||||||||||||||||
| |||||||||||||||||||
| D1-like |
| ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| D2-like |
| ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Receptor (ligands) |
| ||||||||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Transporter (inhibitors) |
| ||||||||||||||
| Enzyme (inhibitors) |
| ||||||||||||||
| Others |
| ||||||||||||||
This article is issued from Wikipedia - version of the 9/23/2016. The text is available under the Creative Commons Attribution/Share Alike but additional terms may apply for the media files.