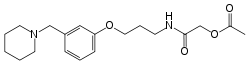
Roxatidine acetate
 | |
| Clinical data | |
|---|---|
| Routes of administration | Oral |
| ATC code | A02BA06 (WHO) |
| Pharmacokinetic data | |
| Bioavailability | 80–90% |
| Protein binding | 5–7% |
| Metabolism |
Hepatic deacetylation Minor involvement of CYP2D6 and CYP2A6 |
| Biological half-life | 5–7 hours |
| Excretion | Renal |
| Identifiers | |
| |
| CAS Number |
78628-28-1 |
| PubChem (CID) | 5105 |
| DrugBank |
DB08806 |
| ChemSpider |
4926 |
| UNII |
IV9VHT3YUM |
| KEGG |
D08495 |
| ChEMBL |
CHEMBL46102 |
| Chemical and physical data | |
| Formula | C19H28N2O4 |
| Molar mass | 348.437 g/mol |
| 3D model (Jmol) | Interactive image |
| |
| |
| | |
Roxatidine acetate is a specific and competitive histamine H2 receptor antagonist drug that is used to treat gastric ulcers, Zollinger–Ellison syndrome, erosive esophagitis, gastro-oesophageal reflux disease, and gastritis.[1][2]
Pharmacodynamic studies showed that 150 mg of roxatidine acetate were optimal in suppressing gastric acid secretion, and that a single bedtime dose of 150 mg was more effective than a dose of 75 mg twice daily in terms of inhibiting nocturnal acid secretion.[1]
It is available in countries including China, Japan, Korea, Germany, Italy, the Netherlands, Greece and South Africa.[2]
References
- 1 2 Murdoch D, McTavish D (1991). "Roxatidine acetate. A review of its pharmacodynamic and pharmacokinetic properties, and its therapeutic potential in peptic ulcer disease and related disorders". Drugs. 42 (2): 240–260. doi:10.2165/00003495-199142020-00006. PMID 1717223.
- 1 2 BioSpectrum Bureau 1 November 2012 Sinhuan's generic heart drug gets production approval
This article is issued from Wikipedia - version of the 7/10/2016. The text is available under the Creative Commons Attribution/Share Alike but additional terms may apply for the media files.