Telenzepine
 | |
| Clinical data | |
|---|---|
| ATC code | None |
| Identifiers | |
| |
| CAS Number | 80880-90-6 |
| PubChem (CID) | 5387 |
| ChemSpider | 5194 |
| UNII |
0990EG3K10 |
| ChEMBL | CHEMBL253978 |
| Chemical and physical data | |
| Formula | C19H22N4O2S |
| Molar mass | 370.47 g/mol |
| 3D model (Jmol) | Interactive image |
| |
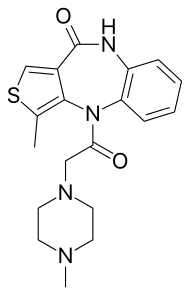
Telenzepine is a thienobenzodiazepine acting as selective M1 antimuscarinic. It is used in the treatment of peptic ulcers.[1] Telenzepine is atropisomeric, in other words the molecule has a stereogenic C–N-axis; in neutral aqueous solution it displays a half-life for racemization of the order of 1000 years. The enantiomers have been resolved. The activity is related to the (+)-isomer which is about 500-fold more active as the (–)-isomer at muscarinic receptors in the rat cerebal cortex.[2]
See also
References
- ↑ Eveleigh, P.; Hulme, E. C.; Schudt, C.; Birdsall, N. J. (1989). "The existence of stable enantiomers of telenzepine and their stereoselective interaction with muscarinic receptor subtypes". Molecular Pharmacology. 35 (4): 477–483. PMID 2704371.
- ↑ Clayden, J.; Moran, W. J.; Edwards, P. J.; Laplante, S. R. (2009). "The Challenge of Atropisomerism in Drug Discovery". Angewandte Chemie International Edition. 48 (35): 6398–6401. doi:10.1002/anie.200901719. PMID 19637174.
External links
- "Telenzepine is at least 25 times more potent than pirenzepine—a dose response and comparative secretory study in man". Gut. 28: 888–95. 1987. doi:10.1136/gut.28.7.888. PMC 1433086
 . PMID 3653758.
. PMID 3653758.
| Classes |
|
|---|---|
| Antidepressants (TCAs and TeCAs) |
|
| Antihistamines |
|
| Antipsychotics |
|
| Anticonvulsants | |
| Others |
|
| 1,4-Benzodiazepines |
|
|---|---|
| 1,5-Benzodiazepines | |
| 2,3-Benzodiazepines* | |
| Triazolobenzodiazepines | |
| Imidazobenzodiazepines | |
| Oxazolobenzodiazepines | |
| Thienodiazepines | |
| Thienotriazolodiazepines | |
| Thienobenzodiazepines* | |
| Pyridodiazepines | |
| Pyridotriazolodiazepines | |
| Pyrazolodiazepines | |
| Pyrrolodiazepines | |
| Tetrahydroisoquinobenzodiazepines | |
| Pyrrolobenzodiazepines* | |
| Benzodiazepine prodrugs | |
* atypical activity profile (not GABAA receptor ligands) | |
This article is issued from Wikipedia - version of the 8/31/2016. The text is available under the Creative Commons Attribution/Share Alike but additional terms may apply for the media files.