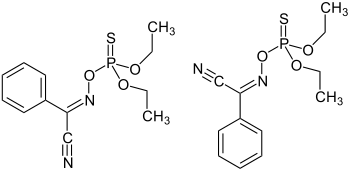
Phoxim
 | |
| Names | |
|---|---|
| IUPAC name
(E,Z)-N-[(Diethoxyphosphorothioyl)oxy]benzenecarboximidoyl cyanide | |
| Other names
Baythion Valexone Phoxime Sebacil Valexon Volaton | |
| Identifiers | |
| 14816-18-3 | |
| 3D model (Jmol) | Interactive image |
| ChemSpider | 25076 |
| ECHA InfoCard | 100.035.337 |
| KEGG | D08373 |
| MeSH | Phoxim |
| PubChem | [https://pubchem.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/compound/9570290
_TEMPHERE_ = ZZZ |
| UNII | 6F5V775VPO |
| |
| |
| Properties | |
| C12H15N2O3PS | |
| Molar mass | 298.30 g·mol−1 |
| Appearance | Brownish red liquid |
| Density | 1.17 g/cm3 |
| Melting point | 6.1 °C (43.0 °F; 279.2 K) |
| Boiling point | 102 |
| 7 ppm | |
| Pharmacology | |
| QP53AE03 (WHO) | |
| Hazards | |
| R-phrases | R22 R50/53 |
| S-phrases | (S2) S36 S60 S61 |
| Except where otherwise noted, data are given for materials in their standard state (at 25 °C [77 °F], 100 kPa). | |
| | |
| Infobox references | |
Phoxim is an organophosphate insecticide that is produced by the Bayer corporation. It is an analogous dimethyl ester and an organothiophosphate acaricide.[2] It is allowed for use in limited applications in the European Union.[3] It is banned for use on crops in the European Union since 22 December 2007.[4]
It is used in veterinary medicine to treat ectoparasitic acarids.
References
- ↑ "Phoxim PubChem entry". Retrieved 2008-07-06.
- ↑ Phoxim Data Sheet
- ↑ Commission for Veterinary Medicinal Products; Phoxim Summary Report
- ↑ COMMISSION DECISION of 21 June 2007 concerning the non-inclusion of certain active substances in Annex I to Council Directive 91/414/EEC and the withdrawal of authorisations for plant protection products containing these substances
External links
- Phoxim in the Pesticide Properties DataBase (PPDB)
This article is issued from Wikipedia - version of the 8/24/2016. The text is available under the Creative Commons Attribution/Share Alike but additional terms may apply for the media files.