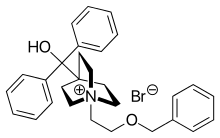
Umeclidinium bromide
 | |
| Clinical data | |
|---|---|
| Trade names | Incruse Ellipta |
| Pregnancy category |
|
| Routes of administration | Inhalation (DPI) |
| ATC code |
R03BB07 (WHO) R03AL03 (WHO) (+vilanterol) |
| Legal status | |
| Legal status |
|
| Pharmacokinetic data | |
| Protein binding | ~89%[1] |
| Metabolism | Hepatic (CYP2D6) |
| Biological half-life | 11 hours |
| Excretion | Feces (58%) and urine (22%) |
| Identifiers | |
| |
| Synonyms | GSK573719A |
| CAS Number | 869113-09-7 |
| PubChem (CID) | 11519069 |
| ChemSpider | 9693857 |
| ChEBI | CHEBI:79040 |
| ECHA InfoCard | 100.166.375 |
| Chemical and physical data | |
| Formula | C29H34BrNO2 |
| Molar mass | 508.49 g/mol |
| 3D model (Jmol) | Interactive image |
| |
| |
Umeclidinium bromide (trade name Incruse Ellipta, GSK) is a long-acting muscarinic antagonist approved for the maintenance treatment of chronic obstructive pulmonary disease (COPD).[1] It is also approved for this indication in combination with vilanterol (as umeclidinium bromide/vilanterol).[2][3]
External links
References
- 1 2 "Incruse Ellipta (umeclidinium inhalation powder) for Oral Inhalation Use. Full Prescribing Information" (PDF). GlaxoSmithKline, Research Triangle Park, NC 27709. Retrieved 22 February 2016.
- ↑ Feldman, GJ; Edin, A (2013). "The combination of umeclidinium bromide and vilanterol in the management of chronic obstructive pulmonary disease: Current evidence and future prospects". Therapeutic advances in respiratory disease. 7 (6): 311–9. doi:10.1177/1753465813499789. PMID 24004659.
- ↑ "FDA Approves Umeclidinium and Vilanterol Combo for COPD". Medscape. December 18, 2013.
This article is issued from Wikipedia - version of the 3/7/2016. The text is available under the Creative Commons Attribution/Share Alike but additional terms may apply for the media files.