Dezocine
 |
| Clinical data |
|---|
| Trade names |
Dalgan |
|---|
| AHFS/Drugs.com |
Micromedex Detailed Consumer Information |
|---|
Routes of
administration |
Intravenous |
|---|
| ATC code |
N02AX03 (WHO) |
|---|
| Legal status |
|---|
| Legal status |
|
|---|
| Pharmacokinetic data |
|---|
| Metabolism |
Hepatic |
|---|
| Biological half-life |
2.2 hours |
|---|
| Identifiers |
|---|
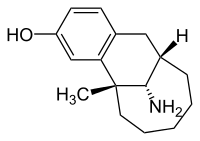
- (5R,11S,13R)-13-Amino-5-methyl-5,6,7,8,9,10,11,12-octahydro-5,11-methanobenzo[10]annulen-3-ol
|
| Synonyms |
WY-16225 |
|---|
| CAS Number |
53648-55-8  Y Y |
|---|
| PubChem (CID) |
3033053 |
|---|
| DrugBank |
DB01209  N N |
|---|
| ChemSpider |
2297867  Y Y |
|---|
| UNII |
VHX8K5SV4X  Y Y |
|---|
| KEGG |
D00838  Y Y |
|---|
| ChEBI |
CHEBI:4474  Y Y |
|---|
| ChEMBL |
CHEMBL1685  Y Y |
|---|
| Chemical and physical data |
|---|
| Formula |
C16H23NO |
|---|
| Molar mass |
245.36 g/mol |
|---|
| 3D model (Jmol) |
Interactive image |
|---|
OC1=CC=C2C([C@]3(CCCCC[C@](C2)([H])[C@@]3([H])N)C)=C1
|
InChI=1S/C16H23NO/c1-16-8-4-2-3-5-12(15(16)17)9-11-6-7-13(18)10-14(11)16/h6-7,10,12,15,18H,2-5,8-9,17H2,1H3/t12-,15-,16+/m0/s1  Y YKey:VTMVHDZWSFQSQP-VBNZEHGJSA-N  Y Y
|
 N N Y (what is this?) (verify) Y (what is this?) (verify) |
|---|
Dezocine (INN, USAN) (brand name Dalgan) is a marketed opioid analgesic of the benzomorphan group.[1] First synthesized in 1970,[2] it acts at mu-, delta-, and kappa-opioid receptors. Dezocine is a mixed agonist/antagonist of opioid receptors. It is related to other benzomorphans such as pentazocine, with a similar profile of effects that include analgesia and euphoria.[3] Unlike many other benzomorphans however, it is a silent antagonist of the κ-opioid receptor, and in accordance, does not produce side effects such as dysphoria or hallucinations at any dose.[4]
History
Dezocine was patented by American Home Products Corp. in 1978. Clinical trials ran from 1979-1985, before its approval by the U.S. Food and Drug Administration (FDA) in 1986. As of 2011,[5] dezocine's usage is discontinued in the United States.
Synthesis
Dezocine [(−)-13β-amino-5,6,7,8,9,10,11,12-octahydro-5α-methyl-5,11-methanobenxocyclodecen-31-ol, hydrobromide] is a pale white crystal powder. It has no apparent odor. The salt is soluble at 20 mg/ml, and a 2% solution has a pH of 4.6.[6]
The synthesis of dezocine begins with the condensation of 1-methyl-7-methoxy-2-tetralone with 1,5-dibromopentane through use of NaH or potassium tertbutylate.[7] This yields 1-(5-bromopentyl)-1-methyl-7-methoxy-2-tetralone, which is then cyclized with NaH to produce 5-methyl-3-methoxy-5,6,7,8,9,10,11,12-octahydro-5,11-methanobenzocyclodecen-13-one. The product is then treated with hydroxylamine hydrochloride, to yield an oxime. A reduction reaction in hydrogen gas produces an isomeric mixture, from which the final product is crystallized and cleaved with HBr.
Legal status in United States
As of 2011, dezocine is not used in the United States or Canada. It is not commercially available in either of these countries,[8] nor is it offered as a prescribed analgesic for postoperative care. In China however, it is commonly used after surgery.[9]
Pharmacology
Target action
Dezocine has an intramuscular bioavailability of 97%.[10] It has a mean t1/2 α of fewer than two minutes, and its half-life is 2.2 hours. Its binding affinity varies with regards to the receptor type, as it acts as a partial agonist primarily on mu-opioid receptors. At kappa-opioid receptors, it acts as an antagonist.[11] Overall, it has a high efficacy as an analgesic.
With regards to its potency, it has a Bmax of 3326 fmol/mg of protein in HEK cells.[9] Dezocine is five times as potent as pethidine and one-fifth as potent as butorphanol.[12]
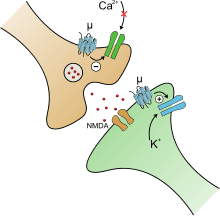
Mechanism of action at the mu opioid receptor
Dezocine is unusual among opiates as it is one of the only primary amines known to be an active opioid (along with bisnortilidine, an active metabolite of tilidine). It is a mixed agonist–antagonist as with other drugs in this class,[13] and despite having a stronger respiratory depressant effect than morphine, dezocine shows a ceiling effect on its respiratory depressive action so above a certain dose this effect does not get any more severe.[14]
Dezocine possesses affinities (Ki) of 3.7 nM, 31.9 nM, and 527 nM for the μ-, κ-, and δ-opioid receptors (MOR, KOR, and DOR), respectively.[15] It is a partial agonist of the MOR and a silent antagonist of the KOR.[15] In addition to its opioid actions, dezocine has been found to act as a serotonin-norepinephrine reuptake inhibitor (SNRI), with pIC50 values of 5.86 for the serotonin transporter (SERT) and 5.68 for the norepinephrine transporter (NET).[15]
Due to its partial agonist nature at the MOR, dezocine has significantly reduced side effects relative to opioid analgesics acting as full agonists of the MOR such as morphine.[15] Moreover, dezocine is not a controlled substance and there are no reports of addiction related to its use, indicating that, unlike virtually all other clinically-employed MOR agonists (including weak partial agonists like buprenorphine) and for reasons that are not fully clear, it is apparently non-addictive.[15]
Administration
Dezocine is generally administered intravenously. It can also be administered in intramuscular doses, and is given singularly rather than continuously. Dezocine has been found to be an effective painkiller comparable to meperidine (pethidine),[16] and so is a more effective analgesic than pentazocine, but causes relatively more respiratory depression than pentazocine.[17] It is a useful drug for the treatment of pain,[18] but side effects such as dizziness limit its clinical application,[19] and it can produce opioid withdrawal syndrome in patients already dependent on other opioids.[20]
Uses
Prescription
Dezocine is generally administered intravenously (as Dalgan) to relieve post-operative pain in patients. Because of its high efficacy, it is often administered at a base dose of 0.1 mg/kg. Respiratory depression, a side-effect of dezocine, reaches a ceiling at 0.3-0.4 mg/kg. It has potent analgesic results, and greater pain-relieving ability than morphine, codeine, and pethidine.[9]
Side effects
Because decozine has mixed agonist/antagonist effects on mu-, delta-, and kappa-opioid receptors, it has a lowered dependence potential than purely agonistic opiates. It can be prescribed, therefore, in small doses over an extended period of time without causing patients to develop and sustain an addiction. Its efficacy as an analgesic is dose-dependent; however, it displays a ceiling effect in induced respiratory depression at 0.3-0.4 mg/kg.
Side effects at lower doses include mild gastrointestinal discomfort and dizziness. It is often administered in post-operative laproscopy patients as an alternative to fentanyl.
See also
References
- ↑ J. Elks (14 November 2014). The Dictionary of Drugs: Chemical Data: Chemical Data, Structures and Bibliographies. Springer. pp. 368–. ISBN 978-1-4757-2085-3.
- ↑ "Espacenet". Espacenet Patent Search.
- ↑ Zacny, J. P.; Lichtor, J. L.; de Wit, H. (1992). "Subjective, Behavioral, and Physiologic Responses to Intravenous Dezocine in Healthy Volunteers". Anesthesia and Analgesia. 74 (4): 523–530. doi:10.1213/00000539-199204000-00010. PMID 1348168.
- ↑ Westmoreland, Cheryl (August 1991). "Opioid agonist-antagonists". Current Opinion in Anesthesiology. 4 (4).
- ↑ "FDA Drugs".
- ↑ Malis, JL; Rosenthale, ME; Gluckman, MI (September 1975). "Animal pharmacology of Wy-16,225, a new analgesic agent.". The Journal of Pharmacology and Experimental Therapeutics. 194 (3): 488–98. PMID 808600.
- ↑ Freed, ME; Potoski, JR; Freed, EH; Conklin, GL; Malis, JL (June 1973). "Bridged aminotetralins as novel potent analgesic sunstances.". Journal of Medicinal Chemistry. 16 (6): 595–9. doi:10.1021/jm00264a003. PMID 4714986.
- ↑ "=FDA Drugs".
- 1 2 3 Gharagozlou, P; Demirci, H; David Clark, J; Lameh, J (Jan 4, 2003). "Activity of opioid ligands in cells expressing cloned mu opioid receptors.". BMC pharmacology. 3: 1. PMC 140036
 . PMID 12513698.
. PMID 12513698. - ↑ Locniskar, A; Greenblatt, DJ; Zinny, MA (1986). "Pharmacokinetics of dezocine, a new analgesic: effect of dose and route of administration.". European journal of clinical pharmacology. 30 (1): 121–3. doi:10.1007/bf00614208. PMID 3709625.
- ↑ Gharagozlou, P; Hashemi, E; DeLorey, TM; Clark, JD; Lameh, J (Jan 25, 2006). "Pharmacological profiles of opioid ligands at kappa opioid receptors.". BMC pharmacology. 6: 3. doi:10.1186/1471-2210-6-3. PMC 1403760
 . PMID 16433932.
. PMID 16433932. - ↑ O'Brien, JJ; Benfield, P (August 1989). "Dezocine. A preliminary review of its pharmacodynamic and pharmacokinetic properties, and therapeutic efficacy.". Drugs. 38 (2): 226–48. doi:10.2165/00003495-198938020-00005. PMID 2670517.
- ↑ Young, A. M.; Stephens, K. R.; Hein, D. W.; Woods, J. H. (1984). "Reinforcing and Discriminative Stimulus Properties of Mixed Agonist-Antagonist Opioids". Journal of Pharmacology and Experimental Therapeutics. 229 (1): 118–126. PMID 6142942.
- ↑ Romagnoli, A.; Keats, A. S. (1984). "Ceiling Respiratory Depression by Dezocine". Clinical Pharmacology and Therapeutics. 35 (3): 367–373. doi:10.1038/clpt.1984.45. PMID 6421529.
- 1 2 3 4 5 Liu, Renyu; Huang, Xi-Ping; Yeliseev, Alexei; Xi, Jin; Roth, Bryan L. (2014). "Novel Molecular Targets of Dezocine and Their Clinical Implications". Anesthesiology. 120 (3): 714–723. doi:10.1097/ALN.0000000000000076. ISSN 0003-3022.
- ↑ Camu, F.; Gepts, E. (1979). "Analgesic Properties of Dezocine for Relief of Postoperative Pain". Acta Anaesthesiologica Belgica. 30 (Suppl): 183–191. PMID 398127.
- ↑ Wuest, H. P.; Bellville, J. W. (1979). "The Respiratory Effects of Dezocine and Pentazocine in Man". Journal of Clinical Pharmacology. 19 (4): 205–210. doi:10.1002/j.1552-4604.1979.tb01653.x. PMID 438355.
- ↑ O'Brien, J. J.; Benfield, P. (1989). "Dezocine. A Preliminary Review of its Pharmacodynamic and Pharmacokinetic Properties, and Therapeutic Efficacy". Drugs. 38 (2): 226–248. doi:10.2165/00003495-198938020-00005. PMID 2670517.
- ↑ Oosterlinck, W.; Verbaeys, A. (1980). "Preliminary Clinical Experience with Dezocine, a New Potent Analgesic". Current Medical Research and Opinion. 6 (7): 472–474. doi:10.1185/03007998009109470. PMID 7363647.
- ↑ Strain, E. C.; Preston, K. L.; Liebson, I. A.; Bigelow, G. E. (1996). "Opioid Antagonist Effects of Dezocine in Opioid-Dependent Humans". Clinical Pharmacology and Therapeutics. 60 (2): 206–217. doi:10.1016/S0009-9236(96)90137-X. PMID 8823239.
|
|---|
|
| MOR |
- PAMs: BMS-986121
- BMS-986122
|
|---|
|
| DOR | |
|---|
|
| KOR |
- Agonists: 6'-GNTI
- 8-CAC
- 18-MC
- 14-Methoxymetopon
- β-Chlornaltrexamine
- β-Funaltrexamine
- Adrenorphin (metorphamide)
- Akuuamicine
- Alazocine
- Allomatrine
- Asimadoline
- BAM-12P
- BAM-18P
- BAM-22P
- Big dynorphin
- Bremazocine
- BRL-52537
- Butorphan
- Butorphanol
- BW-373U86
- Cebranopadol
- Ciprefadol
- CR665
- Cyclazocine
- Cyclorphan
- Cyprenorphine
- Diamorphine (heroin)
- Diacetylnalorphine
- Difelikefalin
- Dihydroetorphine
- Dihydromorphine
- Diprenorphine
- Dynorphin A
- Dynorphin B (rimorphin)
- Eluxadoline
- Enadoline
- Eptazocine
- Erinacine E
- Ethylketazocine
- Etorphine
- Fedotozine
- Fentanyl
- Gemazocine
- GR-89696
- GR-103545
- Hemorphin-4
- Herkinorin
- HS665
- Hydromorphone
- HZ-2
- Ibogaine
- ICI-199,441
- ICI-204,448
- Ketamine
- Ketazocine
- Laudanosine
- Leumorphin (dynorphin B-29)
- Levallorphan
- Levomethorphan
- Levorphanol
- Lexanopadol
- Lofentanil
- LPK-26
- Lufuradom
- Matrine
- MB-1C-OH
- Menthol
- Metazocine
- Metkefamide
- Mianserin
- Mirtazapine
- Morphine
- Moxazocine
- MR-2034
- N-MPPP
- Nalbuphine
- Nalbuphine sebacate
- NalBzOH
- Nalfurafine
- Nalmefene
- Nalodeine (N-allylnorcodeine)
- Nalorphine
- Naltriben
- Niravoline
- Norbuprenorphine
- Norbuprenorphine-3-glucuronide
- Noribogaine
- Norketamine
- O-Desmethyltramadol
- Oripavine
- Oxilorphan
- Oxycodone
- Pentazocine
- Pethidine (meperidine)
- Phenazocine
- Proxorphan
- Racemethorphan
- Racemorphan
- RB-64
- Salvinorin A (salvia)
- Salvinorin B ethoxymethyl ether
- Salvinorin B methoxymethyl ether
- Samidorphan
- SKF-10047
- Spiradoline (U-62,066)
- TH-030418
- Thienorphine
- Tifluadom
- Tricyclic antidepressants (e.g., amitriptyline, desipramine, imipramine, nortriptyline)
- U-50,488
- U-54,494A
- U-69,593
- Xorphanol
|
|---|
|
| NOP | |
|---|
|
| Unsorted | |
|---|
|
| Others |
- Others: Kyotorphin (met-enkephalin releaser/degradation stabilizer)
|
|---|
|
See also: Peptide receptor modulators |
|
|---|
|
| α1 | | |
- Antagonists
- Abanoquil
- Adimolol
- Ajmalicine
- Alfuzosin
- Amosulalol
- Anisodamine
- Arotinolol
- Atiprosin
- Atypical antipsychotics (e.g., clozapine, olanzapine, quetiapine, risperidone)
- Benoxathian
- Buflomedil
- Bunazosin
- Carvedilol
- Corynanthine
- Dapiprazole
- Domesticine
- Doxazosin
- Ergolines (e.g., ergotamine, dihydroergotamine, lisuride, terguride)
- Etoperidone
- Eugenodilol
- Fenspiride
- Hydroxyzine
- Indoramin
- Ketanserin
- L-765,314
- Labetalol
- mCPP
- Mepiprazole
- Metazosin
- Monatepil
- Moxisylyte
- Naftopidil
- Nantenine
- Nefazodone
- Neldazosin
- Niaprazine
- Nicergoline
- Niguldipine
- Pardoprunox
- Pelanserin
- Phendioxan
- Phenoxybenzamine
- Phentolamine
- Piperoxan
- Prazosin
- Quinazosin
- Ritanserin
- Silodosin
- Spiperone
- Talipexole
- Tamsulosin
- Terazosin
- Tiodazosin
- Tolazoline
- Trazodone
- Tetracyclic antidepressants (e.g., amoxapine, maprotiline, mianserin)
- Tricyclic antidepressants (e.g., amitriptyline, clomipramine, doxepin, imipramine, trimipramine)
- Trimazosin
- Typical antipsychotics (e.g., chlorpromazine, fluphenazine, loxapine, thioridazine)
- Urapidil
- WB-4101
- Zolertine
|
|
|---|
|
| α2 | | |
- Antagonists
- 1-PP
- Adimolol
- Aptazapine
- Atipamezole
- Atypical antipsychotics (e.g., asenapine, clozapine, lurasidone, paliperidone, quetiapine, risperidone, zotepine)
- Azapirones (e.g., buspirone, tandospirone)
- BRL-44408
- Buflomedil
- Cirazoline
- Efaroxan
- Esmirtazapine
- Fenmetozole
- Fluparoxan
- Idazoxan
- mCPP
- Mianserin
- Mirtazapine
- NAN-190
- Olanzapine
- Pardoprunox
- Phentolamine
- Phenoxybenzamine
- Piperoxan
- Piribedil
- Rauwolscine
- Rotigotine
- SB-269970
- Setiptiline
- Spiroxatrine
- Sunepitron
- Tolazoline
- Typical antipsychotics (e.g., chlorpromazine, fluphenazine, loxapine, thioridazine)
- Yohimbine
|
|
|---|
|
| β | |
|---|
|
- See also: Dopaminergics
- Melatonergics
- Serotonergics
- Monoamine reuptake and release modulators
- Monoamine metabolism modulators
- Monoamine neurotoxins
|
|
|---|
|
| |
|---|
| | 5-HT1A |
- Agonists: 8-OH-DPAT
- Adatanserin
- Amphetamine
- Antidepressants (e.g., etoperidone, nefazodone, trazodone, vilazodone, vortioxetine)
- Atypical antipsychotics (e.g., aripiprazole, asenapine, clozapine, lurasidone, quetiapine, ziprasidone)
- Azapirones (e.g., buspirone, eptapirone, gepirone, perospirone, tandospirone)
- Bay R 1531
- Befiradol
- BMY-14802
- Cannabidiol
- Dimemebfe
- Dopamine
- Ebalzotan
- Eltoprazine
- Ergolines (e.g., bromocriptine, cabergoline, dihydroergotamine, ergotamine, lisuride, LSD, methylergometrine (methylergonovine), methysergide, pergolide)
- F-11461
- F-12826
- F-13714
- F-14679
- F-15063
- F-15599
- Flesinoxan
- Flibanserin
- Flumexadol
- Lesopitron
- LY-293284
- LY-301317
- mCPP
- MKC-242
- Naluzotan
- NBUMP
- Osemozotan
- Oxaflozane
- Pardoprunox
- Piclozotan
- Rauwolscine
- Repinotan
- Roxindole
- RU-24969
- S-14506
- S-14671
- S-15535
- Sarizotan
- Serotonin (5-HT)
- SSR-181507
- Sunepitron
- Tryptamines (e.g., 5-CT, 5-MeO-DMT, 5-MT, bufotenin, DMT, indorenate, N-Me-5-HT, psilocin, psilocybin)
- TGBA01AD
- U-92016A
- Urapidil
- Vilazodone
- Xaliproden
- Yohimbine
| |
- Antagonists: Atypical antipsychotics (e.g., iloperidone, risperidone, sertindole)
- AV965
- Beta blockers (e.g., alprenolol, cyanopindolol, iodocyanopindolol, oxprenolol, pindobind, pindolol, propranolol, tertatolol)
- BMY-7378
- CSP-2503
- Dotarizine
- Ergolines (e.g., metergoline)
- Flopropione
- GR-46611
- Isamoltane
- Lecozotan
- Mefway
- Metitepine (methiothepin)
- MIN-117 (WF-516)
- MPPF
- NAN-190
- Robalzotan
- S-15535
- SB-649915
- SDZ 216-525
- Spiperone
- Spiramide
- Spiroxatrine
- UH-301
- WAY-100135
- WAY-100635
- Xylamidine
| | |
|
|---|
| | 5-HT1B |
- Agonists: CGS-12066A
- CP-93129
- CP-94253
- CP-122,288
- CP-135807
- Eltoprazine
- Ergolines (e.g., bromocriptine, dihydroergotamine, ergotamine, methylergometrine (methylergonovine), methysergide, pergolide)
- mCPP
- RU-24969
- Serotonin (5-HT)
- Triptans (e.g., avitriptan, donitriptan, eletriptan, sumatriptan, zolmitriptan)
- TFMPP
- Tryptamines (e.g., 5-BT, 5-CT, 5-MT, DMT)
- Vortioxetine
| | | | |
|
|---|
| | 5-HT1D |
- Agonists: CP-122,288
- CP-135807
- CP-286601
- Ergolines (e.g., bromocriptine, cabergoline, dihydroergotamine, ergotamine, LSD, methysergide)
- GR-46611
- L-694247
- L-772405
- mCPP
- PNU-109291
- PNU-142633
- Serotonin (5-HT)
- TGBA01AD
- Triptans (e.g., almotriptan, avitriptan, donitriptan, eletriptan, frovatriptan, naratriptan, rizatriptan, sumatriptan, zolmitriptan)
- Tryptamines (e.g., 5-BT, 5-CT, 5-Et-DMT, 5-MT, 5-(nonyloxy)tryptamine, DMT)
| | | | |
|
|---|
| | 5-HT1E | |
|---|
| | 5-HT1F | |
|---|
|
|
|
| |
|---|
| | 5-HT2A |
- Agonists: 25H/NB series (e.g., 25I-NBF, 25I-NBMD, 25I-NBOH, 25I-NBOMe, 25B-NBOMe, 25C-NBOMe, 25TFM-NBOMe, 2CBCB-NBOMe, 25CN-NBOH, 2CBFly-NBOMe)
- 2Cs (e.g., 2C-B, 2C-E, 2C-I, 2C-T-2, 2C-T-7, 2C-T-21)
- 2C-B-FLY
- 2CB-Ind
- 5-Methoxytryptamines (5-MeO-DET, 5-MeO-DiPT, 5-MeO-DMT, 5-MeO-DPT, 5-MT)
- α-Alkyltryptamines (e.g., 5-Cl-αMT, 5-Fl-αMT, 5-MeO-αET, 5-MeO-αMT, α-Me-5-HT, αET, αMT)
- AL-34662
- AL-37350A
- Bromo-DragonFLY
- Dimemebfe
- DMBMPP
- DOx (e.g., DOB, DOC, DOI, DOM)
- Efavirenz
- Ergolines (e.g., 1P-LSD, ALD-52, bromocriptine, cabergoline, ergine (LSA), ergotamine, lisuride, LA-SS-Az, LSB, LSD, LSD-Pip, LSH, LSP, methylergometrine (methylergonovine), pergolide)
- Flumexadol
- Jimscaline
- Lorcaserin
- MDxx (e.g., MDA, MDMA, MDOH, MMDA)
- O-4310
- Oxaflozane
- PHA-57378
- PNU-22394
- PNU-181731
- RH-34
- Phenethylamines (e.g., lophophine, mescaline)
- Piperazines (e.g., BZP, mCPP, quipazine, TFMPP)
- Serotonin (5-HT)
- TCB-2
- TFMFly
- Tryptamines (e.g., 5-BT, 5-CT, bufotenin, DET, DiPT, DMT, DPT, psilocin, psilocybin, tryptamine)
| |
- Antagonists: 5-I-R91150
- 5-MeO-NBpBrT
- AC-90179
- Adatanserin
- Altanserin
- AMDA
- APD-215
- Atypical antipsychotics (e.g., amperozide, aripiprazole, asenapine, blonanserin, carpipramine, clocapramine, clorotepine, clozapine, fluperlapine, gevotroline, iloperidone, melperone, mosapramine, ocaperidone, olanzapine, paliperidone, quetiapine, risperidone, sertindole, zicronapine, ziprasidone, zotepine)
- Cinanserin
- CSP-2503
- Cyproheptadine
- Deramciclane
- Dotarizine
- Eplivanserin
- Ergolines (e.g., amesergide, LY-53857, LY-215840, mesulergine, metergoline, methysergide, sergolexole)
- Etoperidone
- Fananserin
- Flibanserin
- Glemanserin
- Irindalone
- Ketanserin
- KML-010
- Lubazodone
- LY-393558
- Medifoxamine
- Mepiprazole
- Metitepine (methiothepin)
- MIN-101
- Naftidrofuryl
- Nantenine
- Nefazodone
- Pelanserin
- Phenoxybenzamine
- Pimavanserin
- Pirenperone
- Pizotifen
- Pruvanserin
- Rauwolscine
- Ritanserin
- S-14671
- Sarpogrelate
- Setoperone
- Spiperone
- Spiramide
- SR-46349B
- TGBA01AD
- Teniloxazine
- Temanogrel
- Tetracyclic antidepressants (e.g., amoxapine, aptazapine, esmirtazapine, maprotiline, mianserin, mirtazapine)
- Trazodone
- Tricyclic antidepressants (e.g., amitriptyline)
- Typical antipsychotics (e.g., chlorpromazine, fluphenazine, haloperidol, loxapine, perphenazine, pimozide, pipamperone, prochlorperazine, thioridazine, thiothixene, trifluoperazine)
- Volinanserin
- Xylamidine
- Yohimbine
| | |
|
|---|
| | 5-HT2B |
- Agonists: 4-Methylaminorex
- Aminorex
- Amphetamines (eg., chlorphentermine, cloforex, dexfenfluramine, fenfluramine, levofenfluramine, norfenfluramine)
- BW-723C86
- DOx (e.g., DOB, DOC, DOI, DOM)
- Ergolines (e.g., cabergoline, dihydroergocryptine, dihydroergotamine, ergotamine, methylergometrine (methylergonovine), methysergide, pergolide)
- MDxx (e.g., MDA, MDMA, MDOH, MMDA)
- Piperazines (e.g., mCPP)
- PNU-22394
- Ro60-0175
- Serotonin (5-HT)
- Tryptamines (e.g., 5-BT, 5-CT, 5-MT, α-Me-5-HT, bufotenin, DET, DiPT, DMT, DPT, psilocin, psilocybin, tryptamine)
| | | | |
|
|---|
| | 5-HT2C |
- Agonists: 2Cs (e.g., 2C-B, 2C-E, 2C-I, 2C-T-2, 2C-T-7, 2C-T-21)
- 5-Methoxytryptamines (5-MeO-DET, 5-MeO-DiPT, 5-MeO-DMT, 5-MeO-DPT, 5-MT)
- α-Alkyltryptamines (e.g., 5-Cl-αMT, 5-Fl-αMT, 5-MeO-αET, 5-MeO-αMT, α-Me-5-HT, αET, αMT)
- A-372159
- AL-38022A
- Alstonine
- CP-809101
- Dimemebfe
- DOx (e.g., DOB, DOC, DOI, DOM)
- Ergolines (e.g., ALD-52, cabergoline, dihydroergotamine, ergine (LSA), ergotamine, lisuride, LA-SS-Az, LSB, LSD, LSD-Pip, LSH, LSP, pergolide)
- Flumexadol
- Lorcaserin
- MDxx (e.g., MDA, MDMA, MDOH, MMDA)
- MK-212
- Org 12962
- Org 37684
- Oxaflozane
- PHA-57378
- Phenethylamines (e.g., lophophine, mescaline)
- Piperazines (e.g., aripiprazole, BZP, mCPP, quipazine, TFMPP)
- PNU-22394
- PNU-181731
- Ro60-0175
- Ro60-0213
- Serotonin (5-HT)
- Tryptamines (e.g., 5-BT, 5-CT, bufotenin, DET, DiPT, DMT, DPT, psilocin, psilocybin, tryptamine)
- Vabicaserin
- WAY-629
- WAY-161503
- YM-348
| |
- Antagonists: Adatanserin
- Agomelatine
- Atypical antipsychotics (e.g., asenapine, clorotepine, clozapine, fluperlapine, iloperidone, melperone, olanzapine, paliperidone, quetiapine, risperidone, sertindole, ziprasidone, zotepine)
- Captodiame
- CEPC
- Cinanserin
- Cyproheptadine
- Deramciclane
- Dotarizine
- Eltoprazine
- Ergolines (e.g., amesergide, bromocriptine, LY-53857, LY-215840, mesulergine, metergoline, methysergide, sergolexole)
- Etoperidone
- Fluoxetine
- FR-260010
- Irindalone
- Ketanserin
- Ketotifen
- Latrepirdine (dimebolin)
- Medifoxamine
- Metitepine (methiothepin)
- Nefazodone
- Pirenperone
- Pizotifen
- Propranolol
- Ritanserin
- RS-102221
- S-14671
- SB-200646
- SB-206553
- SB-221284
- SB-228357
- SB-242084
- SB-243213
- SDZ SER-082
- Tedatioxetine
- Tetracyclic antidepressants (e.g., amoxapine, aptazapine, esmirtazapine, maprotiline, mianserin, mirtazapine)
- TIK-301
- Trazodone
- Tricyclic antidepressants (e.g., amitriptyline, nortriptyline)
- Typical antipsychotics (e.g., chlorpromazine, loxapine, pimozide, pipamperone, thioridazine)
- Xylamidine
| | |
|
|---|
|
|
|
| |
|---|
| | 5-HT3 |
- Agonists: Alcohols (e.g., butanol, ethanol, trichloroethanol)
- m-CPBG
- Phenylbiguanide
- Piperazines (e.g., BZP, mCPP, quipazine)
- RS-56812
- Serotonin (5-HT)
- SR-57227
- SR-57227A
- Tryptamines (e.g., 2-Me-5-HT, 5-CT, bufotenidine (5-HTQ))
- Volatiles/gases (e.g., halothane, isoflurane, toluene, trichloroethane)
- YM-31636
| |
- Antagonists: Alosetron
- AS-8112
- Atypical antipsychotics (e.g., clozapine, olanzapine, quetiapine)
- Azasetron
- Batanopride
- Bemesetron (MDL-72222)
- Cilansetron
- CSP-2503
- Dazopride
- Dolasetron
- Galanolactone
- Granisetron
- ICS-205930
- Lerisetron
- Memantine
- Ondansetron
- Palonosetron
- Ramosetron
- Renzapride
- Ricasetron
- Tedatioxetine
- Tetracyclic antidepressants (e.g., amoxapine, mianserin, mirtazapine)
- Thujone
- Tropanserin
- Tropisetron
- Typical antipsychotics (e.g., loxapine)
- Volatiles/gases (e.g., nitrous oxide, sevoflurane, xenon)
- Vortioxetine
- Zacopride
- Zatosetron
| | |
|
|---|
| | 5-HT4 | |
|---|
| | 5-HT5A | |
|---|
| | 5-HT6 |
- Agonists: Ergolines (e.g., dihydroergocryptine, dihydroergotamine, ergotamine, lisuride, LSD, mesulergine, metergoline, methysergide)
- Serotonin (5-HT)
- Tryptamines (e.g., 2-Me-5-HT, 5-BT, 5-CT, 5-MT, Bufotenin, E-6801, E-6837, EMD-386088, EMDT, LY-586713, N-Me-5-HT, tryptamine)
- WAY-181187
- WAY-208466
| |
- Antagonists: ABT-354
- Atypical antipsychotics (e.g., aripiprazole, asenapine, clorotepine, clozapine, fluperlapine, iloperidone, olanzapine, tiospirone)
- AVN-101
- AVN-211
- AVN-322
- AVN-397
- BGC20-760
- BVT-5182
- BVT-74316
- Cerlapirdine
- EGIS-12233
- GW-742457
- Idalopirdine
- Ketanserin
- Latrepirdine (dimebolin)
- Metitepine (methiothepin)
- MS-245
- PRX-07034
- Ritanserin
- Ro04-6790
- Ro 63-0563
- SB-258585
- SB-271046
- SB-357134
- SB-399885
- SB-742457
- Tetracyclic antidepressants (e.g., amoxapine, mianserin)
- Tricyclic antidepressants (e.g., amitriptyline, clomipramine, doxepin, nortriptyline)
- Typical antipsychotics (e.g., chlorpromazine, loxapine)
| | |
|
|---|
| | 5-HT7 | | |
- Antagonists: Atypical antipsychotics (e.g., amisulpride, aripiprazole, asenapine, clorotepine, clozapine, fluperlapine, olanzapine, risperidone, sertindole, tiospirone, ziprasidone, zotepine)
- Butaclamol
- DR-4485
- EGIS-12233
- Ergolines (e.g., 2-Br-LSD (BOL-148), amesergide, bromocriptine, cabergoline, dihydroergotamine, ergotamine, LY-53857, LY-215840, mesulergine, metergoline, methysergide, sergolexole)
- JNJ-18038683
- Ketanserin
- LY-215840
- Metitepine (methiothepin)
- Ritanserin
- SB-258719
- SB-258741
- SB-269970
- SB-656104
- SB-656104A
- SB-691673
- SLV-313
- SLV-314
- Spiperone
- SSR-181507
- Tetracyclic antidepressants (e.g., amoxapine, maprotiline, mianserin, mirtazapine)
- Tricyclic antidepressants (e.g., amitriptyline, clomipramine, imipramine)
- Typical antipsychotics (e.g., acetophenazine, chlorpromazine, chlorprothixene, fluphenazine, loxapine, pimozide)
- Vortioxetine
| | |
|
|---|
|
|
|
- See also: Adrenergics
- Dopaminergics
- Melatonergics
- Monoamine reuptake and release modulators
- Monoamine metabolism modulators
- Monoamine neurotoxins
|


 . PMID 12513698.
. PMID 12513698. . PMID 16433932.
. PMID 16433932.