Exaprolol
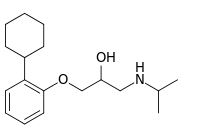 | |
| Names | |
|---|---|
| IUPAC name
1-(2-Cyclohexylphenoxy)-3-(propan-2-ylamino)propan-2-ol | |
| Other names
Esprolol | |
| Identifiers | |
| 55837-19-9 | |
| 3D model (Jmol) | Interactive image |
| ChemSpider | 58934 |
| PubChem | 65485 |
| |
| |
| Properties | |
| C18H29NO2 | |
| Molar mass | 291.44 g·mol−1 |
| Except where otherwise noted, data are given for materials in their standard state (at 25 °C [77 °F], 100 kPa). | |
| Infobox references | |
Exaprolol is a beta-adrenoceptor antagonist.[1]
Synthesis
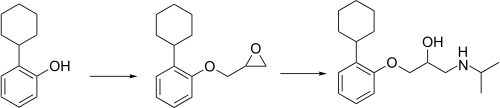
Exaprolol synthesis:[2]
References
- ↑ Van Waarde, A; Doorduin, J; De Jong, JR; Dierckx, RA; Elsinga, PH (2008). "Synthesis and preliminary evaluation of (S)-11C-exaprolol, a novel beta-adrenoceptor ligand for PET". Neurochemistry international. 52 (4–5): 729–33. doi:10.1016/j.neuint.2007.09.009. PMID 17961850.
- ↑ Carissimi, M; Gentili, P; Grumelli, E; Milla, E; Picciola, G; Ravenna, F (1976). "Basic ethers of cyclohexylphenols with beta-blocking activity: Synthesis and pharmacological study of exaprolol". Arzneimittel-Forschung. 26 (4): 506–16. PMID 8056.
This article is issued from Wikipedia - version of the 6/2/2016. The text is available under the Creative Commons Attribution/Share Alike but additional terms may apply for the media files.