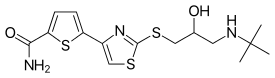
Arotinolol
 | |
| Clinical data | |
|---|---|
| AHFS/Drugs.com | International Drug Names |
| Routes of administration | Oral (tablets) |
| ATC code | none |
| Legal status | |
| Legal status |
|
| Pharmacokinetic data | |
| Bioavailability | 2 hours |
| Biological half-life | 10 hours |
| Identifiers | |
| |
| CAS Number |
41287-43-8 |
| PubChem (CID) | 2239 |
| ChemSpider |
2152 |
| UNII |
394E3P3B99 |
| KEGG |
D07465 |
| ChEMBL |
CHEMBL93298 |
| Chemical and physical data | |
| Formula | C15H21N3O2S3 |
| Molar mass | 371.54 g/mol |
| 3D model (Jmol) | Interactive image |
| |
| |
| | |
Arotinolol (INN, marketed under the tradename Almarl) is a medication in the class of mixed alpha/beta blockers.[1] It also acts as a β3 receptor agonist.[2] A 1979 publication suggests arotinolol as having first been described in the scientific literature by Sumitomo Chemical as "β-adrenergic blocking, antiarrhythmic compound S-596".[3]
Uses
It is used in the treatment of high blood pressure[4] and essential tremor.[5][6]
Recommended dosage is 10–30 mg per day.
References
- ↑ Zhao, Jin; Golozoubova, Valeria; Cannon, Barbara; Nedergaard, Jan (July 2001). "Arotinolol is a weak partial agonist on beta 3-adrenergic receptors in brown adipocytes". Can J Physiol Pharmacol. 79 (7): 585–593. doi:10.1139/cjpp-79-7-585. PMID 11478592.

- ↑ Takahashi, H; Yoshida, T; Nishimura, M; Nakanishi, T; Kondo, M; Yoshimura, M (September 1992). "Beta-3 Adrenergic Agonist, BRL-26830A, and Alpha/Beta Blocker, Arotinolol, Markedly Increase Regional Blood Flow in the Brown Adipose Tissue in Anesthetized Rats". Japanese Circulation Journal. 56 (9): 936–42. doi:10.1253/jcj.56.936. PMID 1383578.
- ↑ Hara, Youichi; Sato, Etsuro; Miyagishi, Akira; Aono, Shunzi; Nakatani, Hiroshi (1979). "新しいβ-受容体遮断薬,dl-2-(3'-t-Butylamino-2'-hydroxypropylthio)-4-(5'-carbamoyl-2'-thienyl)-thiazole hydrochloride (S-596) の薬理作用" [Pharmacological properties of dl-2-(3'-t-butylamino-2'-hydroxypropylthio)-4-(5'-carbamoyl-2'-thienyl)thiazole hydrochloride (S-596), a new β-adrenergic blocking agent]. Folia Pharmacologica Japonica (English abstract) (in Japanese): 707–720. doi:10.1254/fpj.75.707. ISSN 1347-8397.

- ↑ Wu, Haiying; Zhang, Yuqing; Huang, Jianfeng; Zhang, Yuhui; Liu, Guozhang; Sun, Ningling; Yu, Zhenqui; Zhou, Yanrong (September 2001). "Clinical trial of arotinolol in the treatment of hypertension: dippers vs. non-dippers" (PDF). Hypertension Research. 24 (5): 605–10. doi:10.1291/hypres.24.605. ISSN 1348-4214. PMID 11675958.

- ↑ Lee, Kwang-Soo; Kim, Joong-Seok; Kim, Jae-Woo; Lee, Won-Yong; Jeon, Beum-Seok; Kim, Dongjae (August 2003). "A multicenter randomized crossover multiple-dose comparison study of arotinolol and propranolol in essential tremor" (PDF). Parkinsonism & Related Disorders. 9 (6): 341–347. doi:10.1016/S1353-8020(03)00029-4. PMID 12853233.

- ↑ "Almarl (アルマール) Arotinolol HCl Tablets. Full Prescribing Information" (PDF). Sumitomo Dainippon Pharma Co., Ltd. Retrieved 6 March 2016.
External links
- (Japanese) Almarl Full Prescribing Information. Revised November 2009 Sumitomo Dainippon Pharma Co., Ltd.
- (Japanese) Official Sumitomo Dainippon Pharma Website
- https://web.archive.org/web/20110722132720/http://sdic.sookmyung.ac.kr/drug_monograph/view.asp?id=92
This article is issued from Wikipedia - version of the 10/18/2016. The text is available under the Creative Commons Attribution/Share Alike but additional terms may apply for the media files.