Muzolimine
 | |
| Clinical data | |
|---|---|
| ATC code | C03CD01 (WHO) |
| Legal status | |
| Legal status |
|
| Identifiers | |
| |
| CAS Number |
55294-15-0 |
| PubChem (CID) | 41386 |
| ChemSpider |
37766 |
| UNII |
07Z36289ZX |
| KEGG |
D05093 |
| Chemical and physical data | |
| Formula | C11H11Cl2N3O |
| Molar mass | 272.13 g/mol |
| 3D model (Jmol) | Interactive image |
| |
| |
| | |
Muzolimine is a High-ceiling loop diuretic.[1] It is a pyrazole diuretic which was used for treatment of hypertension but was withdrawn worldwide because of severe neurological side effects.[2]
Synthesis
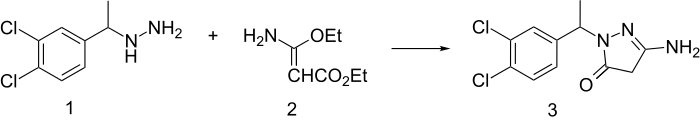
Muzolimine synthesis:[3]
Rxn of (1-(3,4-dichlorophenyl)ethyl)hydrazine (1) with ethyl 3-amino-3-ethoxyacrylate (2) leads to a ring-forming two-site reaction and formation of the pyrazoline diuretic agent, muzolimine (3).
References
- ↑ Wangemann, P.; Braitsch, R.; Greger, R. (1987). "The diuretic effect of muzolimine". Pflugers Archiv : European journal of physiology. 410 (6): 674–676. PMID 3449804.
- ↑ Reyes, A. J.; Leary, W. P. (1993). "Clinicopharmacological reappraisal of the potency of diuretics". Cardiovascular Drugs and Therapy. 7: 23–28. doi:10.1007/BF00877955. PMID 8435374.
- ↑ E. Möller et al., DE 2319278; eidem, U.S. Patent 3,957,814 (1974, 1976 both to Bayer); eidem, Experientia 33, 382 (1977).
This article is issued from Wikipedia - version of the 9/24/2016. The text is available under the Creative Commons Attribution/Share Alike but additional terms may apply for the media files.