Doisynoestrol
 | |
| Clinical data | |
|---|---|
| Routes of administration | Oral |
| Identifiers | |
| |
| Synonyms | Diosynestrol, fenocycline, fenocyclin, phenocyclin, dehydrofolliculinic acid |
| CAS Number | 15372-34-6 |
| PubChem (CID) | 97911 |
| ChemSpider | 88384 |
| Chemical and physical data | |
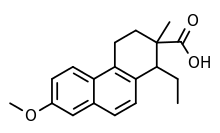
| Formula | C19H22O3 |
| Molar mass | 298.37618 g/mol |
| 3D model (Jmol) | Interactive image |
| |
| |
Doisynoestrol (brand names Fenocyclin, Surestrine, Surestryl; former developmental code name RS-2874), also known as fenocycline, as well as cis-bisdehydrodoisynolic acid 7-methyl ether (BDDA ME), is a synthetic, non-steroidal estrogen of the doisynolic acid group that is no longer marketed.[1][2] It is the methyl ether of bisdehydrodoisynolic acid.[1] Doisynoestrol was described in the literature in 1945.[1]
See also
References
- 1 2 3 J. Elks (14 November 2014). The Dictionary of Drugs: Chemical Data: Chemical Data, Structures and Bibliographies. Springer. pp. 465–. ISBN 978-1-4757-2085-3.
- ↑ Herbai, G. (1971). "SEPARATION OF GROWTH INHIBITING POTENCY FROM OESTROGENICITY IN DIFFERENT WEAK OESTROGENIC DRUGS OF VARIOUS CHEMICAL STRUCTURES". European Journal of Endocrinology. 68 (2): 249–263. doi:10.1530/acta.0.0680249. ISSN 0804-4643.
This article is issued from Wikipedia - version of the 11/12/2016. The text is available under the Creative Commons Attribution/Share Alike but additional terms may apply for the media files.