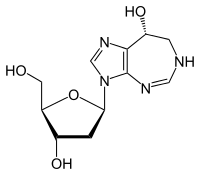
Pentostatin
 | |
 | |
| Clinical data | |
|---|---|
| Trade names | Nipent |
| AHFS/Drugs.com | Monograph |
| MedlinePlus | a692004 |
| Pregnancy category |
|
| Routes of administration | Intravenous |
| ATC code | L01XX08 (WHO) |
| Legal status | |
| Legal status | |
| Pharmacokinetic data | |
| Bioavailability | n/a |
| Protein binding | 4% |
| Metabolism | Hepatic, minor |
| Biological half-life | 2.6 to 16 hours, mean 5.7 hours |
| Identifiers | |
| |
| CAS Number |
53910-25-1 |
| PubChem (CID) | 439693 |
| IUPHAR/BPS | 4805 |
| DrugBank |
DB00552 |
| ChemSpider |
388759 |
| UNII |
395575MZO7 |
| KEGG |
D00155 |
| ChEMBL |
CHEMBL1580 |
| ECHA InfoCard | 100.164.991 |
| Chemical and physical data | |
| Formula | C11H16N4O4 |
| Molar mass | 268.269 g/mol |
| 3D model (Jmol) | Interactive image |
| |
| |
| (verify) | |
Pentostatin (or deoxycoformycin, trade name Nipent, manufactured by SuperGen) is an anticancer chemotherapeutic drug.[1]
Mechanism
It is classified as a purine analog, which is a type of antimetabolite.
It mimics the nucleoside adenosine and thus inhibits the enzyme adenosine deaminase, interfering with the cell's ability to process DNA.[2]
Cancer cells generally divide more often than healthy cells; DNA is highly involved in cell division (mitosis) and drugs which target DNA-related processes are therefore more toxic to cancer cells than healthy cells.
Uses
Pentostatin is used to treat hairy cell leukemia.[3] It is given by intravenous infusion once every two weeks for three to six months.
Additionally, pentostatin has been used to treat steroid-refractory acute and chronic graft-versus-host disease.[4]
Pentostatin is also used in chronic lymphocytic leukemia (CLL) patients who have relapsed.
References
- ↑ Kay NE, Geyer SM, Call TG, et al. (January 2007). "Combination chemoimmunotherapy with pentostatin, cyclophosphamide, and rituximab shows significant clinical activity with low accompanying toxicity in previously untreated B chronic lymphocytic leukemia". Blood. 109 (2): 405–11. doi:10.1182/blood-2006-07-033274. PMC 1785105
 . PMID 17008537.
. PMID 17008537. - ↑ Sauter C, Lamanna N, Weiss MA (September 2008). "Pentostatin in chronic lymphocytic leukemia". Expert Opin Drug Metab Toxicol. 4 (9): 1217–22. doi:10.1517/17425255.4.9.1217. PMID 18721115.
- ↑ Cannon T, Mobarek D, Wegge J, Tabbara IA (October 2008). "Hairy cell leukemia: current concepts". Cancer Invest. 26 (8): 860–5. doi:10.1080/07357900801965034. PMID 18798068.
- ↑ Bolaños-Meade J, Jacobsohn DA, Margolis J, Ogden A, Wientjes MG, Byrd JC, Lucas DM, Anders V, Phelps M, Grever MR, Vogelsang GB (April 2005). "Pentostatin in steroid-refractory acute graft-versus-host disease". J Clin Onc. 23 (12): 2661–8. doi:10.1200/JCO.2005.06.130. PMID 15837980.