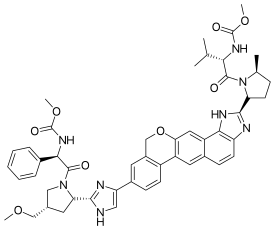
Velpatasvir
 | |
| Clinical data | |
|---|---|
| Trade names | Epclusa, Sofosvel (in combination with sofosbuvir) |
| Routes of administration | Oral (tablets) |
| Legal status | |
| Legal status |
|
| Pharmacokinetic data | |
| Protein binding | >99.5% |
| Metabolism | Liver (CYP2B6, 2C8, 3A4) |
| Biological half-life | 15 hours |
| Excretion | Feces (94%), urine (0.4%)[1] |
| Identifiers | |
| |
| CAS Number | 1377049-84-7 |
| PubChem (CID) | 67683363 |
| DrugBank | DB11613 |
| ChemSpider | 34501056 |
| UNII |
KCU0C7RS7Z |
| ChEBI |
CHEBI:133009 |
| Chemical and physical data | |
| Formula | C49H54N8O8 |
| Molar mass | 883.02 g·mol−1 |
| 3D model (Jmol) | Interactive image |
| |
| |
Velpatasvir is an NS5A inhibitor which is used together with sofosbuvir in the treatment of hepatitis C infection of all six major genotypes.[2]
See also
- Velpatasvir/sofosbuvir, with more information about the drug combination
- Discovery and development of NS5A inhibitors
References
- ↑ "Epclusa (sofosbuvir and velpatasvir) Tablets, for Oral Use. Full Prescribing Information" (PDF). Gilead Sciences, Inc. Foster City, CA 94404. Retrieved 1 August 2016.
- ↑ FDA Approves Epclusa, Drugs.com
This article is issued from Wikipedia - version of the 12/5/2016. The text is available under the Creative Commons Attribution/Share Alike but additional terms may apply for the media files.