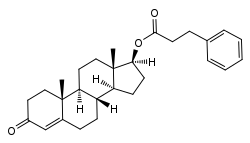
Testosterone phenylpropionate
 | |
| Clinical data | |
|---|---|
| Trade names | Testolent, Sustanon, Omnadren |
| Routes of administration | Intramuscular injection |
| Identifiers | |
| |
| CAS Number | 1255-49-8 |
| PubChem (CID) | 14743 |
| ChemSpider | 14062 |
| UNII | 8GN84GWX51 |
| KEGG | D08574 |
| ChEMBL | CHEMBL2356993 |
| Chemical and physical data | |
| Formula | C28H36O3 |
| Molar mass | 420.58364 g/mol |
| 3D model (Jmol) | Interactive image |
| |
| |
Testosterone phenylpropionate (BAN) (brand name Testolent), or testosterone phenpropionate, also known as testosterone hydrocinnamate, is a synthetic anabolic-androgenic steroid (AAS) and an androgen ester – specifically, the C17β phenylpropionate ester of testosterone – which was formerly marketed in Romania.[1][2][3][4] It was first reported in the scientific literature in 1955 and was an ingredient of several isolated AAS commercial products, but was never widely used.[4] Testosterone phenylpropionate was also notably a component of Sustanon and Omnadren.[4][5]
See also
References
- ↑ J. Elks (14 November 2014). The Dictionary of Drugs: Chemical Data: Chemical Data, Structures and Bibliographies. Springer. pp. 641–642. ISBN 978-1-4757-2085-3.
- ↑ Index Nominum 2000: International Drug Directory. Taylor & Francis. January 2000. ISBN 978-3-88763-075-1.
- ↑ I.K. Morton; Judith M. Hall (6 December 2012). Concise Dictionary of Pharmacological Agents: Properties and Synonyms. Springer Science & Business Media. ISBN 978-94-011-4439-1.
- 1 2 3 William Llewellyn (2011). Anabolics. Molecular Nutrition Llc. pp. 583,697. ISBN 978-0-9828280-1-4.
- ↑ Kenneth L. Becker (2001). Principles and Practice of Endocrinology and Metabolism. Lippincott Williams & Wilkins. pp. 1185–. ISBN 978-0-7817-1750-2.
This article is issued from Wikipedia - version of the 11/30/2016. The text is available under the Creative Commons Attribution/Share Alike but additional terms may apply for the media files.