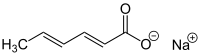
Sodium sorbate
 | |||
| |||
| Names | |||
|---|---|---|---|
| IUPAC name
sodium (2E,4E)-hexa-2,4-dienoate | |||
| Identifiers | |||
| 7757-81-5 | |||
| 3D model (Jmol) | Interactive image | ||
| ChemSpider | 4938659 | ||
| ECHA InfoCard | 100.028.927 | ||
| E number | E201 (preservatives) | ||
| PubChem | 23665582 | ||
| |||
| |||
| Properties | |||
| C6H7NaO2 | |||
| Molar mass | 134.10835 g/mol | ||
| Odor | hydrocarbon-like | ||
| Boiling point | 233 °C (451 °F; 506 K)[1] | ||
| Except where otherwise noted, data are given for materials in their standard state (at 25 °C [77 °F], 100 kPa). | |||
| | |||
| Infobox references | |||
Sodium sorbate is the sodium salt of sorbic acid. Its formula is NaC6H7O2 and systematic name is sodium (E,E)-hexa-2,4-dienoate.
It is a food additive with E-number E201.
Safety and health effects
Unlike other sorbic acid salts such as potassium sorbate (E202) and calcium sorbate (E203), the use of sodium sorbate as a food additive is not allowed in the EU due to potential genotoxic effects.[2]
References
This article is issued from Wikipedia - version of the 12/1/2016. The text is available under the Creative Commons Attribution/Share Alike but additional terms may apply for the media files.