SAM-IV riboswitch
| S-adenosyl methionine (SAM) riboswitch, | |
|---|---|
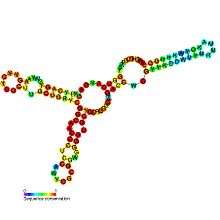 | |
| Predicted secondary structure and sequence conservation of SAM-IV | |
| Identifiers | |
| Symbol | SAM-IV |
| Rfam | RF00634 |
| Other data | |
| RNA type | Cis-reg; riboswitch |
| Domain(s) | Bacteria |
| SO | 0005836 |
SAM-IV riboswitches are a kind of riboswitch that specifically binds S-adenosylmethionine (SAM),[1] a cofactor used in many methylation reactions. Originally identified by bioinformatics,[2] SAM-IV riboswitches are largely confined to the Actinomycetales, an order of Bacteria. Conserved features of SAM-IV riboswitch and experiments imply that they probably share a similar SAM-binding site to another class of SAM-binding riboswitches called SAM-I riboswitches. However, the scaffolds of these two types of riboswitch appear to be quite distinct.
See also
References
- ↑ Weinberg Z, Regulski EE, Hammond MC, et al. (2008). "The aptamer core of SAM-IV riboswitches mimics the ligand-binding site of SAM-I riboswitches". RNA. 14 (5): 822–8. doi:10.1261/rna.988608. PMC 2327355
 . PMID 18369181.
. PMID 18369181. - ↑ Weinberg Z, Barrick JE, Yao Z, et al. (2007). "Identification of 22 candidate structured RNAs in bacteria using the CMfinder comparative genomics pipeline". Nucleic Acids Res. 35 (14): 4809–19. doi:10.1093/nar/gkm487. PMC 1950547
 . PMID 17621584.
. PMID 17621584.
External links
This article is issued from Wikipedia - version of the 9/2/2015. The text is available under the Creative Commons Attribution/Share Alike but additional terms may apply for the media files.