Ratha (architecture)
Plans of the main types of buildings with rathas
In Hindu temple architecture, a ratha is a facet or vertical offset projection on the tower (generally a shikhara).[1]
In Sanskrit, the word "ratha" means "chariot", but the link with this meaning is not clear.
The rathas are decorated with geometric figures or statues, such as statues of a gatekeeper watching outside or a niche with a statue of a deity.
Sometimes, the facet of the ratha is hollowed to the interior; these are rathas with recesses.
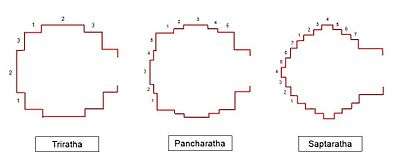
If there is only one facet, this is a temple with three rathas (triratha): the wall and the facet on the left and on the right.
If there are a main facet and a secondary one, the temple has five rathas (pancharatha). There are also temples with seven rathas (saptaratha).[2][3] and nine rathas (navaratha).
Examples of triratha temples
Examples of pancharatha temples
| Pancharatha temples |
|---|
| Isanesvara Siva Temple in Bhubaneswar |
| Jagannath Temple in Baripada |
| Lingaraja Temple in Bhubaneswar |
|
Examples of saptaratha temples
Examples of navaratha temples
See also
- Ratha, for the original meaning of the word
Notes
External links







