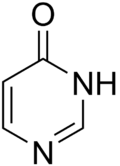
Pyrimidone
 | |
| Names | |
|---|---|
| IUPAC name
Pyrimidone | |
| Other names
Hydroxypyrimidine; Pyrimidinone | |
| Identifiers | |
| 51953-17-4 | |
| 3D model (Jmol) | Interactive image |
| PubChem | 20695 |
| |
| Properties | |
| C4H4N2O | |
| Molar mass | 96.09 g·mol−1 |
| Appearance | White to light yellow powder |
| Melting point | 163 to 168 °C (325 to 334 °F; 436 to 441 K) |
| Hazards | |
| Main hazards | Respiratory system, eye, skin irritation |
| Except where otherwise noted, data are given for materials in their standard state (at 25 °C [77 °F], 100 kPa). | |
| | |
| Infobox references | |
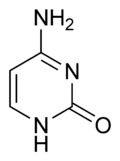
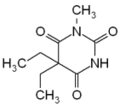
Pyrimidone is the name given to either of two heterocyclic compounds with the formula C4H4N2O: 2-pyrimidone and 4-pyrimidone. The compounds can also be called 2-hydroxypyrimidine or 4-hydroxypyrimidine respectively, based on a substituted pyrimidine, or 1,3-diazine, ring.
Derivatives
Derivatives of pyrimidone are the basis of many other biological molecules, including:
- Nucleobases, such as cytosine
- Barbiturates, such as metharbital
- Antiulcer drugs including temelastine, icotidine, donetidine, and lupitidine.
This article is issued from Wikipedia - version of the 4/10/2016. The text is available under the Creative Commons Attribution/Share Alike but additional terms may apply for the media files.