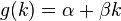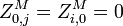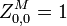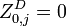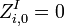Probalign
Probalign is a sequence alignment tool that calculates a maximum expected accuracy alignment using partition function posterior probabilities.[1] Base pair probabilities are estimated using an estimate similar to Boltzmann distribution. The partition function is calculated using a dynamic programming approach.
Algorithm
The following describes the algorithm used by probalign to determine the base pair probabilities.[2]
Alignment score
To score an alignment of two sequences two things are needed:
The score 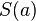 of an alignment a is defined as:
of an alignment a is defined as:
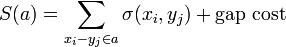
Now the boltzmann weighted score of an alignment a is:
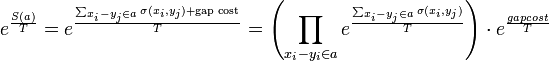
Where 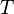 is a scaling factor.
is a scaling factor.
The probability of an alignment assuming boltzmann distribution is given by
![Pr[a|x,y] = \frac{e^{\frac{S(a)}{T}}}{Z}](../I/m/83e5bbc32cf060e02e2b58ec31da7ada.png)
Where 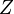 is the partition function, i.e. the sum of the boltzmann weights of all alignments.
is the partition function, i.e. the sum of the boltzmann weights of all alignments.
Dynamic Programming
Let 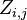 denote the partition function of the prefixes
denote the partition function of the prefixes 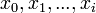 and
and 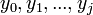 . Three different cases are considered:
. Three different cases are considered:
-
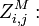 the partition function of all alignments of the two prefixes that end in a match.
the partition function of all alignments of the two prefixes that end in a match. -
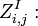 the partition function of all alignments of the two prefixes that end in an insertion
the partition function of all alignments of the two prefixes that end in an insertion 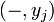 .
. -
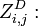 the partition function of all alignments of the two prefixes that end in a deletion
the partition function of all alignments of the two prefixes that end in a deletion 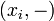 .
.
Then we have: 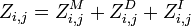
Initialization
The matrixes are initialized as follows:
Recursion
The partition function for the alignments of two sequences 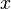 and
and 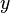 is given by
is given by 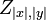 , which can be recursively computed:
, which can be recursively computed:
-
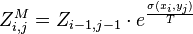
-
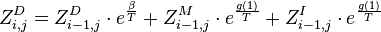
-
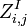 analogously
analogously
Base pair probability
Finally the probability that positions 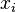 and
and 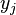 form a base pair is given by:
form a base pair is given by:
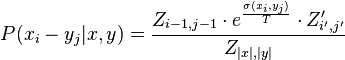
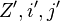 are the respective values for the recalculated
are the respective values for the recalculated 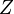 with inversed base pair strings.
with inversed base pair strings.
See also
References
- ↑ U. Roshan and D. R. Livesay, Probalign: multiple sequence alignment using partition function posterior probabilities, Bioinformatics, 22(22):2715-21, 2006 (PDF)
- ↑ Lecture "Bioinformatics II" at University of Freiburg
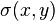 (e.g.
(e.g.