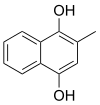
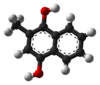
Menadiol
| |||
| Names | |||
|---|---|---|---|
| IUPAC name
2-Methylnaphthalene-1,4-diol | |||
| Other names
2-Methyl-1,4-naphthalenediol; 2-Methyl-1,4-dihydroxynaphthalene | |||
| Identifiers | |||
| 481-85-6 | |||
| 3D model (Jmol) | Interactive image | ||
| ChemSpider | 9794 | ||
| ECHA InfoCard | 100.006.886 | ||
| PubChem | 10209 | ||
| UNII | VQ093653DO | ||
| |||
| |||
| Properties | |||
| C11H10O2 | |||
| Molar mass | 174.20 g·mol−1 | ||
| Except where otherwise noted, data are given for materials in their standard state (at 25 °C [77 °F], 100 kPa). | |||
| Infobox references | |||
Menadiol is an organic compound with the formula C6H4(COH)2(CH)(CH3). It is formally a derivative of p-hydroquinone. It is an intermediate in the synthesis of vitamin K4.[1] It is oxidized to menadione.[2]
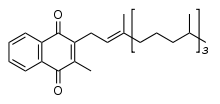
The menadiol core is apparent in the structure of vitamin K.
References
- ↑ Vitamin K, drugs.com
- ↑ Fritz Weber, August Rüttimann "Vitamin K" Ullmann's Encyclopedia Of Industrial Chemistry, 2012, Wiley-VCH, Weinheim. doi:10.1002/14356007.o27_o08
This article is issued from Wikipedia - version of the 7/25/2016. The text is available under the Creative Commons Attribution/Share Alike but additional terms may apply for the media files.