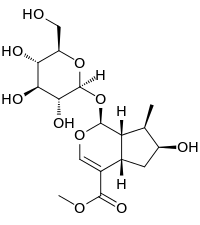
Loganin
 | |
| Names | |
|---|---|
| IUPAC name
(1S,4aS,6S,7R,7aS)-6-Hydroxy-7-methyl-1-[(2S,3R,4S,5S,6R)-3,4,5-trihydroxy-6-(hydroxymethyl)oxan-2-yl]oxy-1,4a,5,6,7,7a-hexahydrocyclopenta[c]pyran-4-carboxylate | |
| Other names
Loganoside | |
| Identifiers | |
| 18524-94-2 | |
| 3D model (Jmol) | Interactive image |
| ChEBI | CHEBI:15771 |
| ChemSpider | 79111 |
| ECHA InfoCard | 100.038.529 |
| EC Number | 242-398-0 |
| KEGG | C01433 |
| PubChem | 87691 |
| |
| |
| Properties | |
| C17H26O10 | |
| Molar mass | 390.39 g·mol−1 |
| Except where otherwise noted, data are given for materials in their standard state (at 25 °C [77 °F], 100 kPa). | |
| Infobox references | |
Loganin is one of the best-known of the iridoid glycosides.It is named for the Loganiaceae,having first been isolated from the seeds of a member of that plant family, namely those of Strychnos nux-vomica. It also occurs in Alstonia boonei (Apocynaceae),[1] a medicinal tree of West Africa and in the medicinal/entheogenic shrub Desfontainia spinosa (Columelliaceae) native to Central America and South America.
Biosynthesis
Loganin is formed from loganic acid by the enzyme loganic acid O-methyltransferase (LAMT). Loganin then becomes a substrate for the enzyme secologanin synthase (SLS) to form secologanin, a secoiridoid monoterpene found as part of ipecac and terpene indole alkaloids.
References
- ↑ Adotey, J. P.; Adukpo, G. E.; Opoku-Boahen, Y.; Armah, F. A. (2012). "A Review of the Ethnobotany and Pharmacological Importance of Alstonia boonei De Wild (Apocynaceae)". ISRN Pharmacology. 2012: 587160. doi:10.5402/2012/587160. PMC 3413980
 . PMID 22900200.
. PMID 22900200.
This article is issued from Wikipedia - version of the 12/13/2015. The text is available under the Creative Commons Attribution/Share Alike but additional terms may apply for the media files.