List of X-ray space telescopes

Chandra (AXAF) checks out a pulsar with its focusing X-ray optics

NuStar's "lens" for focusing X-rays
List of X-ray space telescopes is a listing of "telescopes" in outer space that can observe X-ray wavelengths.
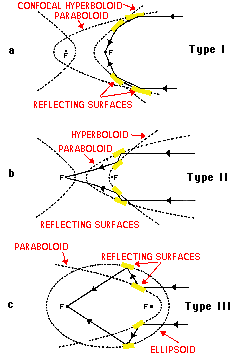
X-rays mirrors can be built, but only if the angle from the plane of reflection is very low (typically 10 arc-minutes to 2 degrees).[1] These are called glancing (or grazing) incidence mirrors. In 1952, Hans Wolter outlined three ways a telescope could be built using only this kind of mirror.[2][3]
- Advanced Satellite for Cosmology and Astrophysics
- Advanced Telescope for High Energy Astrophysics
- AGILE (satellite)
- Apollo Telescope Mount
- Array of Low Energy X-ray Imaging Sensors
- Astronomical Netherlands Satellite
- Astrosat
- BeppoSAX
- Broad Band X-ray Telescope
- Compton Gamma Ray Observatory (detection range extended to hard X-rays)
- Chandra X-ray Observatory
- Constellation-X Observatory
- Einstein Observatory
- EXOSAT
- Ginga (satellite)
- Granat
- Gravity and Extreme Magnetism
- Hakucho
- Hard X-ray Modulation Telescope
- High Energy Astronomy Observatory 1
- High Energy Astronomy Observatory 3
- High Energy Transient Explorer
- Hinode
- Hinotori (satellite)
- Hitomi (Astro-H)
- INTEGRAL
- International X-ray Observatory
- LOFT
- MOXE
- Neutron Star Interior Composition Explorer
- NIXT
- NuSTAR
- PoGOLite
- Reuven Ramaty High Energy Solar Spectroscopic Imager
- ROSAT
- Rossi X-ray Timing Explorer
- Space Variable Objects Monitor
- Spektr-RG
- Suzaku (satellite)
- Swift Gamma-Ray Burst Mission
- Tenma
- Uhuru (satellite)
- Wolter telescope
- X-ray astronomy satellites
- XEUS
- XMM-Newton
- Yohkoh
See also
- Calorimetric Electron Telescope
- Cosmic-ray observatory
- Phase-contrast X-ray imaging
- Wolter telescope
- X-ray astronomy satellites
- X-ray spectroscopy
References
- ↑ Kulinder Pal Singh. "Techniques in X-ray Astronomy" (pdf).
- ↑ Wolter, H. (1952). "Glancing Incidence Mirror Systems as Imaging Optics for X-rays". Annalen der Physik. 10: 94. Bibcode:1952AnP...445...94W. doi:10.1002/andp.19524450108.
- ↑ Wolter, H. (1952). "A Generalized Schwarzschild Mirror System For Use at Glancing Incidence for X-ray Imaging". Annalen der Physik. 10: 286. Bibcode:1952AnP...445..286W. doi:10.1002/andp.19524450410.
This article is issued from Wikipedia - version of the 7/21/2016. The text is available under the Creative Commons Attribution/Share Alike but additional terms may apply for the media files.