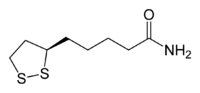
Lipoamide
 | |
 | |
| Names | |
|---|---|
| IUPAC name
5-(1,2-Dithiolan-3-yl)pentanamide | |
| Identifiers | |
| 940-69-2 | |
| 3D model (Jmol) | Interactive image |
| ChEBI | CHEBI:17460 |
| ChemSpider | 5360246 |
| ECHA InfoCard | 100.012.159 |
| MeSH | lipoamide |
| PubChem | 6992093 |
| |
| |
| Properties | |
| C8H15NOS2 | |
| Molar mass | 205.343 g/mol |
| Except where otherwise noted, data are given for materials in their standard state (at 25 °C [77 °F], 100 kPa). | |
| | |
| Infobox references | |
Lipoamide is a trivial name for 6,8-dithiooctanoic amide. It is 6,8-dithiooctanoic acid's functional form where the carboxyl group is attached to protein (or any other amine) by an amide linkage (containing -NH2). Sometimes lipoamide is used to refer to protein bound lipoic acid, but this can be misleading as this is technically incorrect. Lipoyl-protein or lipoyl-domain are better terms to refer to protein bound lipoic acid.
There are no reported occurrences of free lipoamide in nature.
See also
This article is issued from Wikipedia - version of the 3/21/2016. The text is available under the Creative Commons Attribution/Share Alike but additional terms may apply for the media files.