Kepler-69b
| Exoplanet | List of exoplanets | |
|---|---|---|
| Parent star | ||
| Star | Kepler-69 (KOI-172) | |
| Constellation | Cygnus | |
| Right ascension | (α) | 19h 33m 02.62s |
| Declination | (δ) | +42° 52′ 08″ |
| Apparent magnitude | (mV) | 14.0[1] |
| Mass | (m) | 0.98 M☉ |
| Radius | (r) | 0.93 R☉ |
| Temperature | (T) | 5700 (± 100) K |
| Metallicity | [Fe/H] | -0.540 |
| Age | 0.4 Gyr | |
| Physical characteristics | ||
| Radius | (r) | 2.24 R⊕ |
| Temperature | (T) | 779K |
| Orbital elements | ||
| Semi-major axis | (a) | 0.094 AU |
| Eccentricity | (e) | 0.16 |
| Orbital period | (P) | 13.722341 d |
| Inclination | (i) | 89.62° |
| Discovery information | ||
| Discovery date | 17 April 2013 | |
| Discoverer(s) | Barclay et al. | |
| Discovery method | Transit (Kepler Mission) | |
| Discovery site | Kepler Space Observatory | |
| Discovery status | Published refereed article | |
Kepler-69b is the innermost planet of the Kepler-69 system. It is likely a hot super-Earth or mini-Neptune.[1][2]
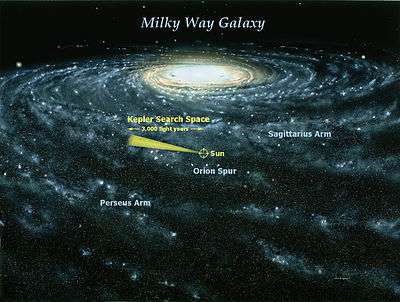
The Kepler Space Telescope search volume, in the context of the Milky Way Galaxy.
References
- 1 2 3 Barclay, Thomas; et al. (2013). "A super-Earth-sized planet orbiting in or near the habitable zone around Sun-like star". The Astrophysical Journal. 768 (2): 101. arXiv:1304.4941
 . Bibcode:2013ApJ...768..101B. doi:10.1088/0004-637X/768/2/101.
. Bibcode:2013ApJ...768..101B. doi:10.1088/0004-637X/768/2/101. - 1 2 Johnson, Michele; Harrington, J.D. (18 April 2013). "NASA's Kepler Discovers Its Smallest 'Habitable Zone' Planets to Date". NASA. Retrieved 18 April 2013.
Coordinates: ![]() 19h 33m 02.622s, +44° 52′ 08.00″
19h 33m 02.622s, +44° 52′ 08.00″
This article is issued from Wikipedia - version of the 8/7/2016. The text is available under the Creative Commons Attribution/Share Alike but additional terms may apply for the media files.


