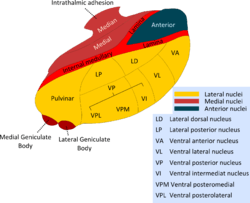
Intralaminar nuclei of thalamus
| Intralaminar nuclei of thalamus | |
|---|---|
 Thalamic nuclei | |
| Details | |
| Identifiers | |
| Latin | nuclei intralaminares thalami |
| MeSH | intralaminar+thalamic+nuclei |
| NeuroNames | hier-300 |
| NeuroLex ID | Intralaminar nuclear group |
| TA | A14.1.08.615 |
| FMA | 62021 |
The intralaminar nuclei are collections of neurons in the thalamus that are generally divided in two groups as follows:[1]
- anterior (rostral) group
- central medial nucleus
- paracentral nucleus
- central lateral nucleus
- posterior (caudal) intralaminar group
- centromedian nucleus
- parafascicular nucleus
Some sources also include a "central dorsal" nucleus.
Degeneration of this area can be associated with progressive supranuclear palsy and Parkinson's disease.[2]
See also
- Central tegmental tract
- Output of the ARAS
References
- ↑ Mancall, E., Brock, D. & Gray, H. (2011). Gray's clinical neuroanatomy the anatomic basis for clinical neuroscience. Philadelphia: Elsevier/Saunders.
- ↑ Henderson JM, Carpenter K, Cartwright H, Halliday GM (July 2000). "Loss of thalamic intralaminar nuclei in progressive supranuclear palsy and Parkinson's disease: clinical and therapeutic implications". Brain. 123 (7): 1410–21. doi:10.1093/brain/123.7.1410. PMID 10869053.
External links
This article is issued from Wikipedia - version of the 8/2/2016. The text is available under the Creative Commons Attribution/Share Alike but additional terms may apply for the media files.