Indoxyl
 | |
 | |
| Names | |
|---|---|
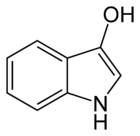
| IUPAC name
1H-Indol-3-ol | |
| Identifiers | |
| 480-93-3 | |
| 3D model (Jmol) | Interactive image |
| ChEBI | CHEBI:17840 |
| ChemSpider | 45861 |
| ECHA InfoCard | 100.216.308 |
| KEGG | C05658 |
| PubChem | 50591 |
| |
| |
| Properties | |
| C8H7NO | |
| Molar mass | 133.14728 |
| Except where otherwise noted, data are given for materials in their standard state (at 25 °C [77 °F], 100 kPa). | |
| | |
| Infobox references | |
In chemistry, indoxyl is a nitrogenous substance with the chemical formula: C8H7NO.[1][2] Indoxyl is isomeric with oxindol and is obtained as an oily liquid.
Indoxyl is obtained from indican, which is a glycoside. The hydrolysis of indican yields β-D-glucose and indoxyl.
Indigo dye is a product of the reaction of indoxyl by a mild oxidizing agent such as atmospheric oxygen.
Indoxyl can be found in urine and is titrated with Obermayer's reagent. Obermayer's reagent is a dilute solution FeCl3 in hydrochloric acid.[3]
References
- ↑ Katritzky, A. R.; Pozharskii, A. F. (2000). Handbook of Heterocyclic Chemistry (2nd ed.). Academic Press. ISBN 0080429882.
- ↑ Clayden, J.; Greeves, N.; Warren, S.; Wothers, P. (2001). Organic Chemistry. Oxford, Oxfordshire: Oxford University Press. ISBN 0-19-850346-6.
- ↑ Lide, David (1998). CRC - Handbook of Chemistry and Physics. CRC press LLC. pp. Section 8 page 3. ISBN 0-8493-0479-2.
This article is issued from Wikipedia - version of the 5/30/2016. The text is available under the Creative Commons Attribution/Share Alike but additional terms may apply for the media files.