Human rhinovirus internal cis-acting regulatory element
| Human rhinovirus internal cis-acting regulatory element (CRE) | |
|---|---|
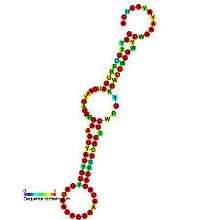 | |
| Predicted secondary structure and sequence conservation of Rhino_CRE | |
| Identifiers | |
| Symbol | Rhino_CRE |
| Rfam | RF00220 |
| Other data | |
| RNA type | Cis-reg |
| Domain(s) | Viruses |
| SO | 0000233 |
Human rhinovirus internal cis-acting regulatory element (CRE) is a CRE from the human rhinoviruses. The CRE is located within the genome segment encoding the capsid proteins so is found in a protein coding region. The element is essential for efficient viral replication and it has been suggested that the CRE is required for initiation of minus-strand RNA synthesis.[1]
See also
- Human parechovirus 1 (HPeV1) cis regulatory element (CRE)
- Rotavirus cis-acting replication element (CRE)
References
- ↑ McKnight, KL; Lemon SM (1998). "The rhinovirus type 14 genome contains an internally located RNA structure that is required for viral replication". RNA. 4 (12): 1569–1584. doi:10.1017/S1355838298981006. PMC 1369726
 . PMID 9848654.
. PMID 9848654.
External links
This article is issued from Wikipedia - version of the 5/12/2014. The text is available under the Creative Commons Attribution/Share Alike but additional terms may apply for the media files.