Hexazinone
 | |
| Names | |
|---|---|
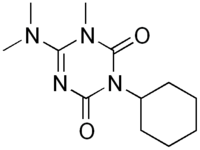
| IUPAC name
3-Cyclohexyl-6-dimethylamino-1-methyl-1,3,5-triazine-2,4-dione | |
| Other names
Velpar Hexazinone | |
| Identifiers | |
| 51235-04-2 | |
| 3D model (Jmol) | Interactive image Interactive image |
| ChemSpider | 36542 |
| ECHA InfoCard | 100.051.869 |
| KEGG | C10926 |
| PubChem | 39965 |
| |
| |
| Properties | |
| C12H20N4O2 | |
| Molar mass | 252.31 |
| Appearance | White crystalline solid |
| Density | 1.25 g/cm3 |
| Melting point | 116 °C (241 °F; 389 K) |
| Soluble | |
| Except where otherwise noted, data are given for materials in their standard state (at 25 °C [77 °F], 100 kPa). | |
| | |
| Infobox references | |
Hexazinone is an organic compound that is used as a broad spectrum herbicide. It is a colorless solid. It exhibits some solubility in water but is highly soluble in most organic solvents except alkanes. A member of the triazine class herbicides, it is manufactured by DuPont and sold under the trade name Velpar.[1]
It functions by inhibiting photosynthesis and thus is a nonselective herbicide. It is used to control grasses, broadleaf, and woody plants. Approximately 33% is used on alfalfa, 31% in forestry, 29% in industrial areas, 4% on rangeland and pastures, and < 2% on sugarcane.[2]
In 1989, hexazinone was deliberately used in an act of vandalism to poison the Treaty Oak in Austin, Texas.
Hexazinone is a pervasive groundwater contaminant, due to its high water solubility.
References
- ↑ Arnold P. Appleby, Franz Müller, Serge Carpy "Weed Control" in Ullmann's Encyclopedia of Industrial Chemistry 2002, Wiley-VCH, Weinheim. doi:10.1002/14356007.a28_165
- ↑ Hexazinone, Herbicide Profile, Pesticide Management Education Program, Cornell University
External links
- DuPont webpage on Velpar
- Hexazinone in the Pesticide Properties DataBase (PPDB)