Heptene
| | |
| Names | |
|---|---|
| IUPAC name
hept-1-ene | |
| Identifiers | |
| 592-76-7 | |
| 3D model (Jmol) | Interactive image |
| ChemSpider | 11121 |
| ECHA InfoCard | 100.008.881 |
| PubChem | 11610 |
| |
| |
| Properties[1] | |
| C7H14 | |
| Molar mass | 98.19 g·mol−1 |
| Appearance | Colorless liquid |
| Density | 0.697 g/mL |
| Melting point | −119 °C (−182 °F; 154 K) |
| Boiling point | 94 °C (201 °F; 367 K) |
| Hazards[1] | |
| R-phrases | R11 R36/37/38 R65 |
| S-phrases | S16 S26 S36 S62 |
| Flash point | −9 °C (16 °F; 264 K) |
| Except where otherwise noted, data are given for materials in their standard state (at 25 °C [77 °F], 100 kPa). | |
| | |
| Infobox references | |
Heptene is a higher olefin, or alkene with the formula C7H14. The commercial product is a liquid that is a mixture of isomers. It is used as an additive in lubricants, as a catalyst, and as a surfactant. This chemical is also known as heptylene.
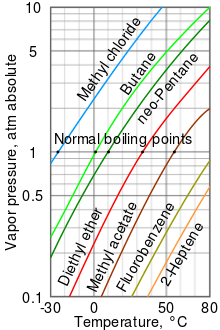
A log-lin vapor pressure chart of Heptene compared with various liquids
References
- 1 2 1-Heptene at Sigma-Aldrich
This article is issued from Wikipedia - version of the 9/22/2016. The text is available under the Creative Commons Attribution/Share Alike but additional terms may apply for the media files.