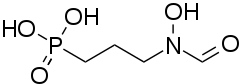
Fosmidomycin
 | |
 | |
| Clinical data | |
|---|---|
| ATC code | none |
| Identifiers | |
| |
| CAS Number |
66508-53-0 |
| PubChem (CID) | 572 |
| DrugBank |
DB02948 |
| ChemSpider |
555 |
| UNII |
5829E3D9I9 |
| ChEBI |
CHEBI:443725 |
| ChEMBL |
CHEMBL203125 |
| Chemical and physical data | |
| Formula | C4H10NO5P |
| Molar mass | 183.100 g/mol |
| 3D model (Jmol) | Interactive image |
| |
| |
| | |
Fosmidomycin is an antibiotic that was originally isolated from culture broths of bacteria of the genus Streptomyces.[1] It specifically inhibits DXP reductoisomerase, a key enzyme in the non-mevalonate pathway of isoprenoid biosynthesis. It is a structural analogue of 2-C-methyl-D-erythrose 4-phosphate. It inhibits the E. coli enzyme with a KI value of 38 nM (4), MTB at 80 nM, and the Francisella enzyme at 99 nM.[2]
Use in malaria
The discovery of the non-mevalonate pathway in malaria parasites has indicated the use of fosmidomycin and other such inhibitors as antimalarial drugs.[3] Indeed, fosmidomycin has been tested in combination treatment with clindamycin for treatment of malaria with favorable results.[4][5][6] It has been shown that an increase in copy number of the target enzyme (DXP reductoisomerase) correlates with in vitro fosmidomycin resistance in the lethal malaria parasite, Plasmodium falciparum.[7]
References
- ↑ Iguchi, E; Okuhara, M; Kohsaka, M; Aoki, H; Imanaka, H (1980). "Studies on new phosphonic acid antibiotics. II. Taxonomic studies on producing organisms of the phosphonic acid and related compounds.". The Journal of antibiotics. 33 (1): 19–23. doi:10.7164/antibiotics.33.18. PMID 7372546.
- ↑ Jawaid, S., Seidle, H., Zhou W, Abdirahman, H., Abadeer, M, Hix, JH, van Hoek, ML and RD Couch. Kinetic Characterization and Phosphoregulation of the Francisella tularensis 1-Deoxy-D-Xylulose 5-Phosphoate Reductoisomerase (MEP Synthase), PLOS One, 4(12): e8288. doi:10.1371/journal.pone.0008288
- ↑ Jomaa, H; et al. (1999). "Inhibitors of the nonmevalonate pathway of isoprenoid biosynthesis as antimalarial drugs". Science. 285 (5433): 1573–6. doi:10.1126/science.285.5433.1573. PMID 10477522.
- ↑ Borrmann, S; et al. (2004). "Fosmidomycin-clindamycin for Plasmodium falciparum infections in African children". J Infect Dis. 189 (5): 901–8. doi:10.1086/381785. PMID 14976608.
- ↑ Borrmann, S; et al. (2006). "Fosmidomycin plus clindamycin for treatment of pediatric patients aged 1 to 14 years with Plasmodium falciparum malaria". Antimicrob Agents Chemother. 50 (8): 2713–8. doi:10.1128/AAC.00392-06. PMC 1538678
 . PMID 16870763.
. PMID 16870763. - ↑ Ruangweerayut, R; et al. (2008). "Assessment of the pharmacokinetics and dynamics of two combination regimens of fosmidomycin-clindamycin in patients with acute uncomplicated falciparum malaria". Malaria J. 7 (1): 225. doi:10.1186/1475-2875-7-225. PMC 2600645
 . PMID 18973702.
. PMID 18973702. - ↑ Dharia, NV; et al. (2009). "Use of high-density tiling microarrays to globally identify mutations and elucidate mechanisms of drug resistance in Plasmodium falciparum". Genome Biology. 10 (2): R21. doi:10.1186/gb-2009-10-2-r21. PMC 2688282
 . PMID 19216790.
. PMID 19216790.