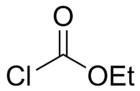
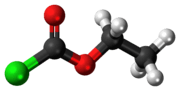
Ethyl chloroformate
 | |
 | |
| Names | |
|---|---|
| Preferred IUPAC name
Ethyl carbonochloridate | |
| Other names
Chloroformic acid ethyl ester Cathyl chloride Ethyl chlorocarbonate | |
| Identifiers | |
| 541-41-3 | |
| 3D model (Jmol) | Interactive image |
| ChemSpider | 10465 |
| ECHA InfoCard | 100.007.981 |
| PubChem | 10928 |
| |
| |
| Properties | |
| C3H5ClO2 | |
| Molar mass | 108.52 g/mol |
| Appearance | Clear liquid |
| Density | 1.1403 g/cm3 |
| Boiling point | 95 °C (203 °F; 368 K) |
| Decomposes | |
| Hazards | |
| Main hazards | Corrosive Flammable |
| NFPA 704 | |
| Flash point | 61 °C (142 °F; 334 K) |
| Except where otherwise noted, data are given for materials in their standard state (at 25 °C [77 °F], 100 kPa). | |
| | |
| Infobox references | |
Ethyl chloroformate is the ethyl ester of chloroformic acid. It is a reagent used in organic synthesis for the introduction of the ethyl carbamate protecting group[2] and for the formation of carboxylic anhydrides.
References
- ↑ Merck Index, 11th Edition, 3742.
- ↑ Protective Groups in Organic Synthesis, Third Edition, Theodora W. Greene and Peter G. M. Wuts, pages 504-506, ISBN 0-471-16019-9
This article is issued from Wikipedia - version of the 9/15/2016. The text is available under the Creative Commons Attribution/Share Alike but additional terms may apply for the media files.
