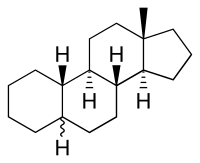
Estrane
 | |
| Names | |
|---|---|
| IUPAC name
Estrane | |
| Systematic IUPAC name
15-Methyltetracyclo[8.7.0.02,7.011,15] heptadecane | |
| Identifiers | |
| 3D model (Jmol) | Interactive image |
| 3125721 | |
| ChEBI | CHEBI:23966 |
| ChemSpider | 11179505 4574149 (1R,2S,10R,11S,15S)-15-methyl,heptadec 5256802 (1R,2S,7R,10R,11S,15S)-15-methyl,heptadec 5256794 (1R,2S,7S,10R,11S,15S)-15-methyl,heptadec |
| PubChem | 12313694 5460658 (1R,2S,10R,11S,15S)-15-methyl,heptadec 6857465 (1R,2S,7R,10R,11S,15S)-15-methyl,heptadec 6857457 (1R,2S,7S,10R,11S,15S)-15-methyl,heptadec |
| |
| |
| Properties | |
| C18H30 | |
| Molar mass | 246.44 g·mol−1 |
| Except where otherwise noted, data are given for materials in their standard state (at 25 °C [77 °F], 100 kPa). | |
| | |
| Infobox references | |
Not to be confused with estrone.
Estrane is a C18 steroid derivative, with a gonane core. The most well known estranes are estrogens like estradiol.
Estrenes are estrane derivatives that contain a double bond. An example is nandrolone.[1]
See also
References
- ↑ Estrenes at the US National Library of Medicine Medical Subject Headings (MeSH)
This article is issued from Wikipedia - version of the 10/31/2016. The text is available under the Creative Commons Attribution/Share Alike but additional terms may apply for the media files.