ELQ-300
 | |
| Names | |
|---|---|
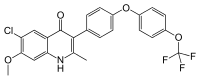
| IUPAC name
6-chloro-7-methoxy-2-methyl-3-{4-[4-(trifluoromethoxy)phenoxy]phenyl}quinolin-4(1H)-one | |
| Identifiers | |
| 3D model (Jmol) | Interactive image |
| ChemSpider | 28540481 |
| |
| |
| Properties | |
| C24H17ClF3NO4 | |
| Molar mass | 475.844 |
| Except where otherwise noted, data are given for materials in their standard state (at 25 °C [77 °F], 100 kPa). | |
| Infobox references | |
ELQ-300 is an experimental antimalarial medication. It is an endochin-like quinolone and the first in a new class of antimalarials known as quinolone-3-diarylethers.[1]
ELQ-300 acts as an inhibitor of the mitochondrial cytochrome bc1 complex (complex III in the electron transport chain).[1] In preclinical studies with mice, it was found to be highly active against Plasmodium falciparum and Plasmodium vivax at all life cycle stages that play a role in the transmission of malaria, and to have good oral bioavailability.[1]
References
Further reading
- "NIH-Supported Researchers Identify New Class of Malaria Compounds" (Press release). U.S. National Institutes of Health. March 20, 2013.
This article is issued from Wikipedia - version of the 7/7/2015. The text is available under the Creative Commons Attribution/Share Alike but additional terms may apply for the media files.