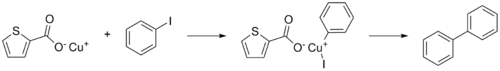Copper(I)-thiophene-2-carboxylate
"CuTC" redirects here. For other uses, see CUTC (disambiguation).
-thiophene-2-carboxylate.png) | |
| Names | |
|---|---|
| IUPAC name
Copper(I) thiophene-2-carboxylate | |
| Other names
CuTC | |
| Identifiers | |
| 68986-76-5 | |
| 3D model (Jmol) | Interactive image Interactive image |
| ChemSpider | 9369899 |
| ECHA InfoCard | 100.161.358 |
| PubChem | 11194830 |
| |
| |
| Properties | |
| C5H3CuO2S | |
| Molar mass | 190.68 g·mol−1 |
| Hazards | |
| Main hazards | Irritant (Xi) |
| R-phrases | R36/37/38 |
| S-phrases | S26 |
| US health exposure limits (NIOSH): | |
| PEL (Permissible) |
TWA 1 mg/m3 (as Cu)[2] |
| REL (Recommended) |
TWA 1 mg/m3 (as Cu)[2] |
| IDLH (Immediate danger) |
TWA 100 mg/m3 (as Cu)[2] |
| Except where otherwise noted, data are given for materials in their standard state (at 25 °C [77 °F], 100 kPa). | |
| | |
| Infobox references | |
Copper(I)-thiophene-2-carboxylate or CuTC is a thiophene and a reagent in organic chemistry that especially promotes the Ullmann reaction between aryl halides.[3]
References
- ↑ Copper(I) thiophene-2-carboxylate at Sigma-Aldrich
- 1 2 3 "NIOSH Pocket Guide to Chemical Hazards #0150". National Institute for Occupational Safety and Health (NIOSH).
- ↑ Jwanro Hassan; Marc Sévignon; Christel Gozzi; Emmanuelle Schulz; Marc Lemaire (2002). "Aryl-Aryl Bond Formation One Century after the Discovery of the Ullmann Reaction" (PDF). Chem. Rev. 102 (5): 1359–1470. doi:10.1021/cr000664r. PMID 11996540.
This article is issued from Wikipedia - version of the 5/29/2016. The text is available under the Creative Commons Attribution/Share Alike but additional terms may apply for the media files.