Classification schemes for Southeast Asian languages
There have been various classification schemes for Southeast Asian languages (see the articles for the respective language families). Language families include:
A number of language groups in Arunachal Pradesh traditionally considered to be Sino-Tibetan (Tibeto-Burman) may in fact constitute independent language families or isolates (Roger Blench 2011). (See Language isolates and independent language families in Arunachal)
Macrofamilies
Austro-Tai links the Austronesian and Tai-Kadai languages. Austric links the languages of Southeast Asia apart from Sino-Tibetan. Sagart proposes instead Sino-Austronesian, linking Austronesian and Sino-Tibetan; Starosta proposed a family called East Asian that covered both this and Austric. Genetic similarities between the peoples of East and Southeast Asia have led some to speculate about "Haplogroup O" languages. In a different direction, the Dené–Caucasian hypothesis links Sino-Tibetan to languages of Siberia (Dene–Yeniseian) and the Caucasus.
Proto-languages
- Proto-Austronesian
- Proto-Tai–Kadai language
- Proto-Kra
- Proto-Kam–Sui language
- Proto-Hlai
- Proto-Tai
- Proto-Austroasiatic language
- Proto-Mon–Khmer
- Proto-Munda language
- Proto-Sino-Tibetan language
- Proto-Hmong–Mien
Comparison
The following table compares the phonemic inventories of various recently reconstructed proto-languages of Southeast Asia.
| Proto-language | Proto-Kra | Proto-Tai | Proto-Hlai | Proto-S. Tai–Kadai | Proto-Austronesian | Proto-Tibeto-Burman | Proto-Mon–Khmer |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Source | Ostapirat (2000) | Pittayaporn (2009)[1] | Norquest (2007)[2] | Norquest (2007)[2] | Blust (2009)[3] | Matisoff (2003)[4] | Shorto (2006)[5] |
| Consonants | 32 | 33–36 | 32 | 28–29 | 25 | 23 | 21 |
| Vowels | 6 | 7 | 4–5 | 5–7 | 4 | 5–6 | 7 |
| Diphthongs | 4 | 5 | – | 1+ | 4 | 2+ | 3 |
| Consonantal finals | 7 | 10–11 | – | – | – | 6 | – |
| Vowel length contrast |
No | Yes | Yes | Yes | No | Yes | Yes |
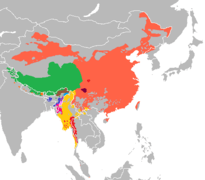
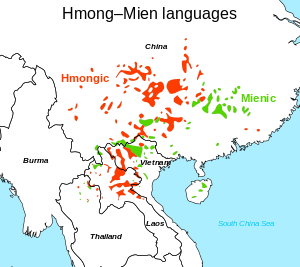
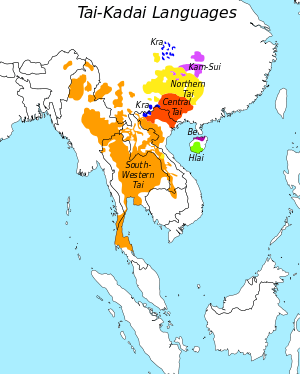
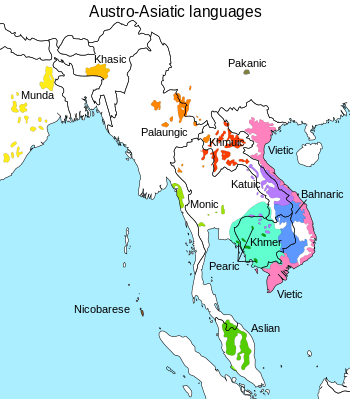
Maps of language families
|
See also
- Languages of China
- Haplogroup O (Y-DNA)#Languages families and genes
- SEAlang library
- Writing systems of Southeast Asia
- Category:Linguists of the Southeast Asian languages
- Category:Linguists of the Austronesian languages
External links
- Hartmann, John (Professor of Thai). "Outline: Spoken and Written Languages of Southeast Asia." Northern Illinois University.
- Migliazza, Brian. 2004. Southeast Asia Language Families.
| Bahnaric |
| ||||||||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Katuic | |||||||||||||||
| Vietic | |||||||||||||||
| Khmuic | |||||||||||||||
| Palaungic |
| ||||||||||||||
| Khasic | |||||||||||||||
| Pakanic | |||||||||||||||
| Khmeric | |||||||||||||||
| Pearic | |||||||||||||||
| Monic | |||||||||||||||
| Aslian |
| ||||||||||||||
| Nicobaric | |||||||||||||||
| Shompen | |||||||||||||||
| Munda |
| ||||||||||||||
| Kra | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Kam–Sui | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Hlai | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Ong Be | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Tai (Zhuang) |
| ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| (Proto-language) | |||||||||||||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Hmongic |
| ||||||||||||||||||
| Mienic | |||||||||||||||||||
| Mixed languages | |||||||||||||||||||
Sino-Tibetan branches | |||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Western Himalayas | |||||||
| Eastern Himalayas | |||||||
| Naga Hills |
| ||||||
| East Asia |
| ||||||
| Dubious (possible isolates) | |||||||
| Proposed groupings | |||||||
| Proto-languages | |||||||
| Bodish |
| ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| West Himalayish | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Tamangic | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Western "Pro-" | |
|---|---|
| Central "Ro-" | |
| Eastern "Yak-" | |
| Eastern | |
|---|---|
| Western | |
| Unclassified | |
| Kukish (Kuki-Chin) |
| ||||||||||||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Karbi | |||||||||||||||||||
| Ao | |||||||||||||||||||
| Angami–Pochuri | |||||||||||||||||||
| Tangkhul | |||||||||||||||||||
| Zeme | |||||||||||||||||||
| Meithei | |||||||||||||||||||
| Unclassified | |||||||||||||||||||
| Ersuic | |||
|---|---|---|---|
| Naic (Naxish) ? | |||
| Core Qiangic |
| ||
| Mixed | |||
Cross (†) and italics indicate extinct languages. | |||
| Mondzish | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Burmish |
| ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Loloish |
| ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Unclassified | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Major subdivisions |
| ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Standardized forms | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Phonology | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| History | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Literary forms |
| ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Scripts |
| ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Rukaic | 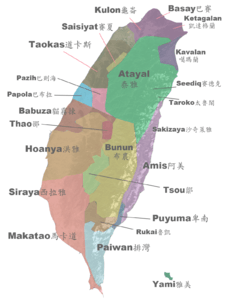 | ||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Tsouic | |||||||
| Northern Formosan |
| ||||||
| East Formosan | |||||||
| Southern | |||||||
| |||||||
| Malayo-Sumbawan |
| ||||||||||||||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Northwest Sumatran |
| ||||||||||||||||||||
| Lampungic |
| ||||||||||||||||||||
| Celebic (Disputed) |
| ||||||||||||||||||||
| South Sulawesi | |||||||||||||||||||||
| Moken | |||||||||||||||||||||
| Javanese |
| ||||||||||||||||||||
| Central–Eastern Malayo-Polynesian (over 700 languages) |
| ||||||||||||||||||||
| Unclassified | |||||||||||||||||||||
| Nuclear Micronesian |
| ||||||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Non-Nuclear | |||||||||||||
| Polynesian |
| ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Fijian |
| ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Other | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Africa |
| ||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Europe and Asia |
| ||||||
| New Guinea and the Pacific |
| ||||||
| Australia |
| ||||||
| North America |
| ||||||
| Mesoamerica |
| ||||||
| South America |
| ||||||
| See also | |||||||
Families with more than 30 languages are in bold. Families in italics have no living members. | |||||||
| Sovereign states |
|
|---|---|
| States with limited recognition | |
| Dependencies and other territories |
|
Notes
- ↑ Pittayaporn, Pittayawat. 2009. The Phonology of Proto-Tai. Ph.D. dissertation. Department of Linguistics, Cornell University.
- 1 2 Norquest, Peter K. 2007. A Phonological Reconstruction of Proto-Hlai. Ph.D. dissertation. Tucson: Department of Anthropology, University of Arizona.
- ↑ Blust, Robert A. 2009. The Austronesian Languages. Canberra: Pacific Linguistics, Research School of Pacific and Asian Studies, Australian National University. ISBN 0-85883-602-5, ISBN 978-0-85883-602-0.
- ↑ Matisoff, James. 2003. Handbook of Proto-Tibeto-Burman: System and Philosophy of Sino-Tibetan Reconstruction. University of California publications in linguistics, v. 135. Berkeley: University of California Press.
- ↑ Shorto, Harry L., et al. 2006. A Mon–Khmer Comparative Dictionary. Canberra: Australian National University. Pacific Linguistics. ISBN 0-85883-570-3.
| Africa |
| ||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Europe and Asia |
| ||||||
| New Guinea and the Pacific |
| ||||||
| Australia |
| ||||||
| North America |
| ||||||
| Mesoamerica |
| ||||||
| South America |
| ||||||
| See also | |||||||
Families with more than 30 languages are in bold. Families in italics have no living members. | |||||||