Cilofungin
 | |
| Names | |
|---|---|
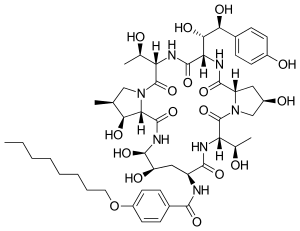
| IUPAC name
N-[(11R,20R,21R,25S,26S)-6-[(1S,2S)-1,2-Dihydroxy-2-(4-hydroxyphenyl)ethyl]-11,20,21,25-tetrahydroxy-3,15-bis(1-hydroxyethyl)-26-methyl-2,5,8,14,17,23-hexaoxo-1,4,7,13,16,22-hexaazatricyclo[22.3.0.09,13]heptacosan-18-yl]-4-(octyloxy)benzamide | |
| Other names | |
| Identifiers | |
| 79404-91-4 | |
| 3D model (Jmol) | Interactive image |
| ChEMBL | ChEMBL2103748 |
| ChemSpider | 5293334 |
| MeSH | Cilofungin |
| PubChem | 6918120 |
| UNII | 8ZJC54A39X |
| |
| |
| Properties | |
| C49H71N7O17 | |
| Molar mass | 1030.12474 |
| Except where otherwise noted, data are given for materials in their standard state (at 25 °C [77 °F], 100 kPa). | |
| | |
| Infobox references | |
Cilofungin (INN)[1] is the first clinically applied member of the echinocandin family of antifungal drugs. It was derived from a fungus in the genus Aspergillus. It accomplishes this by interfering with an invading fungus' ability to synthesize the cell wall (specifically, it inhibits the synthesis of (1→3)-β-D-glucan).[2]
References
- 1 2 3 "International Nonproprietary Names for Pharmaceutical Substances (INN). Recommended International Nonproprietary Names (Rec. INN): List 29" (PDF). World Health Organization.
- ↑ Hudler, George (1998). Magical Mushrooms, Mischievous Molds. Princeton, New Jersey: Princeton University Press. p. 112. ISBN 978-0-691-07016-2.
This article is issued from Wikipedia - version of the 11/13/2016. The text is available under the Creative Commons Attribution/Share Alike but additional terms may apply for the media files.