Bisphenol AF
 | |
| Names | |
|---|---|
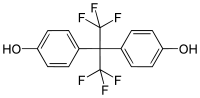
| IUPAC name
4-[1,1,1,3,3,3-Hexafluoro-2-(4-hydroxyphenyl)propan-2-yl]phenol | |
| Other names
Biphenol AF; Hexafluorobisphenol A; Hexafluorodiphenylolpropane; Bisphenol A hexafluoride; 4,4'-(Hexafluoroisopropylidene)diphenol; Hexafluoroacetone bisphenol A; 2,2-Bis(4-hydroxyphenyl)hexafluoropropane | |
| Identifiers | |
| 1478-61-1 | |
| 3D model (Jmol) | Interactive image |
| Abbreviations | BPAF |
| ChemSpider | 66498 |
| ECHA InfoCard | 100.014.579 |
| PubChem | 73864 |
| |
| |
| Properties | |
| C15H10F6O2 | |
| Molar mass | 336.23 g·mol−1 |
| Except where otherwise noted, data are given for materials in their standard state (at 25 °C [77 °F], 100 kPa). | |
| | |
| Infobox references | |
Bisphenol AF (BPAF) is a fluorinated organic compound related to bisphenol A in which the two methyl groups are replaced with trifluoromethyl groups.
Whereas BPA binds with human estrogen-related receptor gamma (ERR-γ), BPAF all but ignores ERR-γ. Instead, BPAF activates ERR-α and binds to and disables ERR-β.[1]
See also
References
- ↑ Janet Raloff: Another plastics ingredient raises safety concerns, Science News, June 5th, 2010; Vol.177 #12 (p. 14)
This article is issued from Wikipedia - version of the 9/5/2015. The text is available under the Creative Commons Attribution/Share Alike but additional terms may apply for the media files.