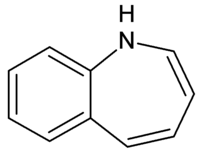
Benzazepine
 | |
 | |
| Names | |
|---|---|
| IUPAC name
1H-benzo[b]azepine | |
| Identifiers | |
| 264-54-0 | |
| 3D model (Jmol) | Interactive image |
| ChEBI | CHEBI:38430 |
| ChemSpider | 10610937 |
| |
| |
| Properties | |
| C10H9N | |
| Molar mass | 143.19 g·mol−1 |
| Except where otherwise noted, data are given for materials in their standard state (at 25 °C [77 °F], 100 kPa). | |
| | |
| Infobox references | |
Benzazepines are heterocyclic chemical compounds consisting of a benzene ring fused to an azepine ring.[1] Examples include benazepril, fenoldopam, lorcaserin and varenicline.
See also
References
- ↑ Benzazepines at the US National Library of Medicine Medical Subject Headings (MeSH)
This article is issued from Wikipedia - version of the 9/27/2015. The text is available under the Creative Commons Attribution/Share Alike but additional terms may apply for the media files.