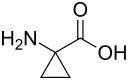
1-Aminocyclopropane-1-carboxylic acid
1-Aminocyclopropane-1-carboxylic acid
 |
| Names |
| Other names
1-Aminocyclopropanecarboxylic acid |
| Identifiers |
| |
22059-21-8  N N |
| 3D model (Jmol) |
[1]: Interactive image
Interactive image |
| Abbreviations |
ACC |
| ChEBI |
CHEBI:58360  Y Y |
| ChEMBL |
ChEMBL265325  Y Y |
| ChemSpider |
520  Y Y |
| DrugBank |
DB02085  Y Y |
| ECHA InfoCard |
100.108.227 |
| KEGG |
C01234  Y Y |
| PubChem |
535 |
InChI=1S/C4H7NO2/c5-4(1-2-4)3(6)7/h1-2,5H2,(H,6,7)  Y YKey: PAJPWUMXBYXFCZ-UHFFFAOYSA-N  Y YInChI=1/C4H7NO2/c5-4(1-2-4)3(6)7/h1-2,5H2,(H,6,7) Key: PAJPWUMXBYXFCZ-UHFFFAOYAF
|
| |
| Properties |
| |
C4H7NO2 |
| Molar mass |
101.1 c |
Except where otherwise noted, data are given for materials in their standard state (at 25 °C [77 °F], 100 kPa). |
 N verify (what is N verify (what is  Y Y N ?) N ?) |
| Infobox references |
|
|
1-Aminocyclopropane-1-carboxylic acid (ACC) is a disubstituted cyclic α-amino acid in which a three-membered cyclopropane ring is fused to the Cα atom of the amino acid.
ACC plays an important role in the biosynthesis of the plant hormone ethylene.[2][3] It is synthesized by the enzyme ACC synthase ( EC 4.4.1.14) from methionine and converted to ethylene by ACC oxidase (EC 1.14.17.4).[4]
ACC is also an exogenous partial agonist of the mammalian NMDA receptor.[5]
References
- 1 2 Caspi R, Foerster H, Fulcher CA, Hopkinson R, Ingraham J, Kaipa P, Krummenacker M, Paley S, Pick J, Rhee SY, Tissier C, Zhang P, Karp PD (2006). "MetaCyc: a multiorganism database of metabolic pathways and enzymes". Nucleic Acids Res. 34 (Database issue): D511–6. doi:10.1093/nar/gkj128. PMC 1347490
 . PMID 16381923.
. PMID 16381923. - ↑ Yang S, Hoffman N (1984). "Ethylene biosynthesis and its regulation in higher plants". Annu. Rev. Plant Physiol. 35: 155–189. doi:10.1146/annurev.pp.35.060184.001103.
- ↑ Kende H (1993). "Ethylene biosynthesis". Annu. Rev. Plant Physiol. 44: 283–307. doi:10.1146/annurev.pp.44.060193.001435.
- ↑ Kende H (1989). "Enzymes of Ethylene Biosynthesis". Plant Physiol. 91 (1): 1–4. doi:10.1104/pp.91.1.1. PMC 1061940
 . PMID 16666977.
. PMID 16666977. - ↑ Inanobe A, Furukawa H, Gouaux E (2005). "Mechanism of partial agonist action at the NR1 subunit of NMDA receptors". Neuron. 47 (1): 71–84. doi:10.1016/j.neuron.2005.05.022. PMID 15996549.
|
|---|
|
Receptor
(ligands) | | AMPA | |
|---|
| | NMDA |
- Antagonists: Competitive antagonists: AP5 (APV)
- AP7
- CGP-37849
- CGP-39551
- CGP-39653
- CGP-40116
- CGS-19755
- CPP
- LY-233,053
- LY-235,959
- LY-274,614
- MDL-100,453
- Midafotel (d-CPPene)
- NPC-12,626
- NPC-17,742
- PBPD
- PEAQX
- Perzinfotel
- PPDA
- SDZ-220581
- Selfotel; Noncompetitive antagonists: ARR-15,896
- Caroverine
- Dexanabinol
- FPL-12495
- FR-115,427
- Hodgkinsine
- Magnesium
- MDL-27,266
- NPS-1506
- Psychotridine
- Zinc; Uncompetitive pore blockers: 2-MDP
- 3-HO-PCP
- 3-MeO-PCE
- 3-MeO-PCMo
- 3-MeO-PCP
- 4-MeO-PCP
- 8A-PDHQ
- 18-MC
- α-Endopsychosin
- Alaproclate
- Amantadine
- Aptiganel
- Arketamine
- ARL-12,495
- ARL-15,896-AR
- ARL-16,247
- Budipine
- Conaridine
- Delucemine
- Dexoxadrol
- Dextrallorphan
- Dieticyclidine
- Diphenidine
- Dizocilpine
- Ephenidine
- Esketamine
- Etoxadrol
- Eticyclidine
- Fluorolintane
- Gacyclidine
- Ibogaine
- Ibogamine
- Indantadol
- Ketamine
- Ketobemidone
- Lanicemine
- Loperamide
- Memantine
- Methadone (Levomethadone)
- Methorphan (Dextromethorphan
- Levomethorphan)
- Methoxetamine
- Methoxphenidine
- Milnacipran
- Morphanol (Dextrorphan
- Levorphanol)
- NEFA
- Neramexane
- Nitromemantine
- Nitrous oxide
- Noribogaine
- Norketamine
- Orphenadrine
- PCPr
- Pethidine (meperidine)
- Phencyclamine
- Phencyclidine
- Propoxyphene
- Remacemide
- Rhynchophylline
- Rimantadine
- Rolicyclidine
- Sabeluzole
- Tabernanthine
- Tenocyclidine
- Tiletamine
- Tramadol
- Xenon; Glycine site antagonists: 4-Cl-KYN (AV-101)
- 5,7-DCKA
- 7-CKA
- ACC
- ACEA-1011
- ACEA-1328
- AV-101
- Carisoprodol
- CGP-39653
- CNQX
- DNQX
- Felbamate
- Gavestinel
- GV-196,771
- Kynurenic acid
- Kynurenine
- L-689,560
- L-701,324
- Licostinel (ACEA-1021)
- LU-73,068
- MDL-105,519
- Meprobamate
- MRZ 2/576
- PNQX
- ZD-9379; NR2B subunit antagonists: Besonprodil
- CERC-301 (MK-0657)
- CO-101,244 (PD-174,494)
- Eliprodil
- Haloperidol
- Ifenprodil
- Isoxsuprine
- Nylidrin
- Ro8-4304
- Ro25-6981
- Traxoprodil; Polyamine site antagonists: Arcaine
- Co 101676
- Diaminopropane
- Diethylenetriamine
- Huperzine A
- Putrescine
- Ro 25-6981; Unclassified/unsorted antagonists: Bumetanide
- Chloroform
- Cyclopropane
- D-αAA
- Diethyl ether
- Enflurane
- Ethanol
- Flufenamic acid
- Flupirtine
- Furosemide
- Halothane
- Isoflurane
- Metaphit
- Methoxyflurane
- Niflumic acid
- Pentamidine isethionate
- Piretanide
- Toluene
- Transcrocetin (saffron)
- Trichloroethane
- Trichloroethanol
- Trichloroethylene
- Xylene
|
|---|
| | Kainate | |
|---|
| | mGlu1 | |
|---|
| | mGlu2 | |
|---|
| | mGlu3 | |
|---|
| | mGlu4 |
- Antagonists: CPPG
- MAP4
- MPPG
- MSOP
- MTPG
- UBP-1112
|
|---|
| | mGlu5 | |
|---|
| | mGlu6 |
- Antagonists: CPPG
- MAP4
- MPPG
- MSOP
- MTPG
- UBP-1112
|
|---|
| | mGlu7 |
- Antagonists: CPPG
- MAP4
- MMPIP
- MPPG
- MSOP
- MTPG
- UBP-1112
|
|---|
| | mGlu8 |
- Antagonists: CPPG
- MAP4
- MPPG
- MSOP
- MTPG
- UBP-1112
|
|---|
|
|---|
|
Transporter
(blockers) | |
|---|
|
Enzyme
(inhibitors) | |
|---|
|
| Others | |
|---|
|
See also: GABAergics • GHBergics • Glycinergics |

 . PMID 16381923.
. PMID 16381923. . PMID 16666977.
. PMID 16666977.