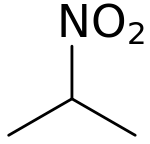
2-Nitropropane
 | |
 | |
| Names | |
|---|---|
| IUPAC name
2-Nitropropane | |
| Identifiers | |
| 79-46-9 | |
| 3D model (Jmol) | Interactive image |
| Abbreviations | 2-NP |
| ChEBI | CHEBI:16037 |
| ChemSpider | 387 |
| ECHA InfoCard | 100.001.100 |
| EC Number | 201-209-1 |
| PubChem | 398 |
| |
| |
| Properties | |
| C3H7NO2 | |
| Molar mass | 89.09 g·mol−1 |
| Appearance | Colorless liquid[1] |
| Odor | Pleasant, fruity[2] |
| Density | 0.9821 g/cm3 |
| Melting point | −91.3 °C (−132.3 °F; 181.8 K) |
| Boiling point | 120.2 °C (248.4 °F; 393.3 K) |
| 17 g/L[1] | |
| Solubility | soluble in chloroform |
| log P | 0.93 |
| Vapor pressure | 13 mmHg (20°C)[2] |
| Acidity (pKa) | 7.68 |
| Refractive index (nD) |
1.3944 (20 °C) |
| Viscosity | 0.721 cP |
| Hazards | |
| NFPA 704 | |
| Flash point | 24 °C (75 °F; 297 K) (open cup) 39 °C (closed cup) |
| 428 °C (802 °F; 701 K) | |
| Explosive limits | 2.6-11.0%[2] |
| Lethal dose or concentration (LD, LC): | |
| LD50 (median dose) |
720 mg/kg |
| LC50 (median concentration) |
2703 ppm (mouse, 2 hr) 400 ppm (rat, 6 hr)[3] |
| LCLo (lowest published) |
714 ppm (cat, 5 hr) 2381 ppm (rabbit, 5 hr) 4622 ppm (guinea pig, 5 hr) 2353 ppm (cat, 1 hr)[3] |
| US health exposure limits (NIOSH): | |
| PEL (Permissible) |
TWA 25 ppm (90 mg/m3)[2] |
| REL (Recommended) |
Ca[2] |
| IDLH (Immediate danger) |
Ca [100 ppm][2] |
| Except where otherwise noted, data are given for materials in their standard state (at 25 °C [77 °F], 100 kPa). | |
| Infobox references | |
2-Nitropropane (2-NP) is a solvent. It is a colorless liquid and is classified as a nitro compound.
Preparation
2-NP is produced by the high-temperature vapor-phase nitration of propane, usually with impurities of 1-nitropropane. 2-NP is also produced as a volatile by-product that can be captured during Leonard's ring-closure hydantoin preparation [4]
Uses
2-NP is used primarily as a solvent and chemical intermediate. It is used in inks, paints, adhesives, varnishes, polymers, resins, fuel, and coatings.[5]
2-NP is also used as a feedstock for other industrial chemicals.[5]
2-NP has uses in the synthesis of phentermine, chlorphentermine, as well as in the synthesis of Teclozan, etc.
Safety
Based on studies in animals, 2-NP is reasonably anticipated to be a human carcinogen[5] and it is listed as an IARC Group 2B carcinogen.[6]
References
- 1 2 Record in the GESTIS Substance Database of the IFA
- 1 2 3 4 5 6 "NIOSH Pocket Guide to Chemical Hazards #0460". National Institute for Occupational Safety and Health (NIOSH).
- 1 2 "2-Nitropropane". Immediately Dangerous to Life and Health. National Institute for Occupational Safety and Health (NIOSH).
- ↑ M. J. Leonard, A. R. Lingham, J. O. Niere, N. R. C. Jackson, P. G. McKay and H. M. Hϋgel (6 Mar 2014). "Alternative synthesis of the anti-baldness compound RU58841". RSC Advances. 4: 14143–14148. doi:10.1039/c4ra00332b.
- 1 2 3 "Report on Carcinogens" (PDF) (Twelfth ed.). National Toxicology Program, Department of Health and Human Services. 2011.
- ↑ Agents Classified by the IARC Monographs
